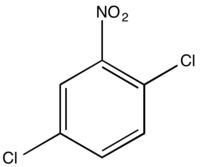
1,4-Dichloro-2-nitrobenzene
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,4-Dichloro-2-nitrobenzene | |
| Identifiers | |
| 89-61-2 | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.749 |
| Properties | |
| C6H3Cl2NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 192.00 |
| Melting point | 52-54 °C |
| Boiling point | 266-269 °C |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
1,4-Dichloro-2-nitrobenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H3Cl2NO2. One of several isomers of dichloronitrobenzene, it is a colorless solid that is insoluble in water. It is produced by nitration of 1,4-dichlorobenzene. It is a precursor to many derivatives of commercial interest. Hydrogenation gives 1,4-dichloroaniline. Nucleophiles displace the chloride adjacent to the nitro group: ammonia gives the aniline derivative, aqueous base gives the phenol derivative, and methoxide gives the anisole derivative. These compounds are respectively 4-chloro-2-nitroaniline, 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol, and 4-chloro-2-nitroanisole.[1] Isomeric with this compound is 1,2-dichloro-4-nitrobenzene.
References
- ↑ Gerald Booth (2007). "Nitro Compounds, Aromatic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/8/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.