1851 Atlantic hurricane season
 | |
| Season summary map | |
| First system formed | June 25, 1851 |
|---|---|
| Last system dissipated | October 19, 1851 |
| Strongest storm1 | Four – – 115 mph (185 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| Total storms | 6 |
| Hurricanes | 3 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) | 1 |
| Total fatalities | 23 direct, 1 indirect |
| Total damage | $60,000 (1851 USD) |
| 1Strongest storm is determined by lowest pressure | |
1840s, 1850, 1851, 1852, 1853 | |
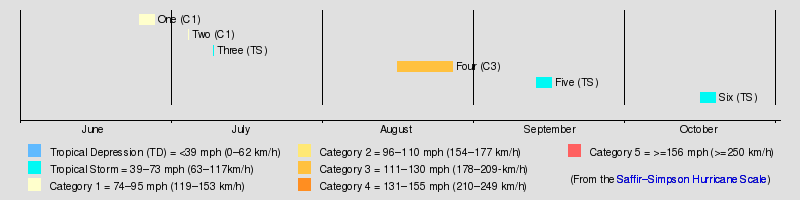
The 1851 Atlantic hurricane season was the first Atlantic hurricane season to be included in the official Atlantic tropical cyclone record.[1] Six known tropical cyclones occurred during the season, the earliest of which formed on June 25 and the latest of which dissipated on October 19. These dates fall within the range of most Atlantic tropical cyclone activity. None of the cyclones existed simultaneously with another. Of the six storms, two only have a single point in their track known.
Two other hurricanes were reported during the season, one near Tampico and the other near Jamaica; however, they are not in the official hurricane database. There may have been other unconfirmed tropical cyclones during the season. Meteorologist Christopher Landsea estimates that between zero and six storms were missed from the official database, due to small tropical cyclone size, sparse ship reports, and relatively unpopulated coastlines.[2]
Season summary
Five of the six tropical cyclones affected land, including three making landfall with winds of over 74 mph (119 km/h). The first struck Texas as a hurricane, which caused moderate to heavy damage, particularly to shipping in Matagorda Bay. One death was indirectly related to the hurricane, as well as at least two injuries.[3]
The strongest and deadliest hurricane of the season tracked from east of the Lesser Antilles, through the Greater Antilles, and across the southeastern United States before last being observed near Newfoundland; it was tied for having the longest duration for a hurricane prior to 1870.[1] When it hit near Panama City, Florida with winds of 115 mph (185 km/h), it caused at least 23 deaths, including five when a lighthouse was destroyed. Many houses were destroyed along its path, primarily along the Florida Panhandle.[4]
The other landfalling hurricane was one that struck near Tampico, where it caused heavy damage. The last tropical storm of the season made landfall on Rhode Island, though associated damage is unknown. A tropical storm affected the Lesser Antilles in early July, and another tropical storm remained nearly stationary for three days to the southeast of North Carolina.[3]
Timeline
Storms
Hurricane One
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | June 25 – June 28 | ||
| Peak intensity | 90 mph (150 km/h) (1-min) 977 mbar (hPa) | ||
A small 90 mph (150 km/h) hurricane was first observed on June 25, about 75 miles (120 km/h) southeast of Freeport, Texas. It tracked westward, moving ashore near Matagorda Bay later that night near peak intensity, with an estimated minimum barometric central pressure of 977 mbar; due to lack of observations, it is possible the hurricane struck as the equivalent of a Category 2 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson scale. The cyclone slowly weakened as it turned northwestward, with hurricane-force wind gusts reported 24 hours after landfall in current-day Medina County. It is estimated that the storm dissipated early on June 28 over central Texas.[3]
The hurricane produced heavy damage near where it moved ashore, having been described as the most disastrous experienced there to date. The winds destroyed every wharf and several houses in Port Lavaca. On Matagorda Island, the saltwater contaminated the fresh water supply, and in Matagorda Bay, heavy shipping losses were reported. As the cyclone progressed inland, it dropped light to moderate rainfall, peaking at around 3 inches (75 mm) in Corpus Christi. A fort near current day Laredo reported 2.48 inches (63 mm) of precipitation. Across its path, the winds downed several trees and houses, leaving two people injured and contributing to a death when a sick person was exposed to the storm.[3]
Hurricane Two
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | July 5 – July 6 | ||
| Peak intensity | 90 mph (150 km/h) (1-min) | ||
A moderate hurricane made landfall near Tampico, which was described as having moved ashore before July 7; the Hurricane Research Division assessed the date as July 5. Heavy damage was reported in Tampico.[3]
Tropical Storm Three
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | July 10 – July 10 | ||
| Peak intensity | 60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min) | ||
A tropical storm passed through the southern Lesser Antilles on July 10. Overall documentation on the storm was weak, and its track elsewhere is unknown.[3]
Hurricane Four
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | August 16 – August 27 | ||
| Peak intensity | 115 mph (185 km/h) (1-min) 960 mbar (hPa) | ||
The fourth known tropical cyclone of the season, also known as the San Agapito Hurricane[5] and the Great Middle Florida Hurricane of August 1851, the storm was first observed on August 16 about 775 miles (1250 km) east of Barbados. It tracked west-northwestward, attaining hurricane status on August 17 as it approached the Lesser Antilles. Shortly thereafter, the hurricane passed between Antigua and Saint Kitts and later south of Saint Croix.[3] On August 18 it brushed the southern coast of Puerto Rico, though it affected the entire island due to a large size of the storm.[5] The next day it made landfall on the southern coast of the Dominican Republic. The cyclone rapidly weakened to tropical storm status over Hispaniola, though it regained hurricane status as it paralleled the southern coast of Cuba just offshore. Late on August 20, the cyclone crossed western Cuba, briefly weakening to tropical storm status before again regaining hurricane status in the southeastern Gulf of Mexico. It quickly strengthened and reached peak winds of 115 mph (185 km/h) early on August 23 about 215 miles (345 km) south-southeast of Pensacola, Florida. Turning northeastward, the hurricane moved ashore near Panama City, Florida at peak intensity,[3] with an estimated barometric pressure of 960 mbar.[6] It accelerated across the Southeastern United States, weakening to a tropical storm before exiting North Carolina into the Atlantic Ocean on August 25. On August 27, it was last observed over Newfoundland as a weak tropical storm.[3]
The hurricane passed near Saint Lucia on August 17,[3] where high tides and rough seas were reported.[7] Flooding was reported in northern Puerto Rico during its passage.[5] Impact is unknown in Hispaniola and Cuba.[3] The hurricane produced an estimated storm tide of 12 feet (3.7 m) at Saint Marks;[3] the combination of waves and the storm tide flooded coastal areas, destroying 50% of the cotton crops in some areas.[4] Rough seas destroyed a brig, killing 17 people, and another person drowned due to a shipwreck. Many ships were expected to have been lost in the storm, resulting in fear of potentially hundreds of deaths. The storm caused heavy damage along the coastline, and in Apalachicola the winds destroyed the roofs of all but two or three buildings. Dog Island Light was destroyed, resulting in five deaths. Further inland, many houses were blown over in Tallahassee, totaling $60,000 in damage (1851 USD). Heavy damage was reported in Alabama, including destroyed crops and damaged houses; damage in the state was less than in Florida.[4] Hurricane-force winds extended into southwestern Georgia,[3] while tropical storm force winds were reported along the coastline. In Savannah, the winds damaged many houses and downed many trees.[8] In North Carolina and Virginia, winds from the storm destroyed crop fields and small buildings; in the region, it was described as the worst storm in 30 years.[9] Storm damage was reported as far north as Cambridge, Massachusetts.[7]
Tropical Storm Five
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | September 13 – September 16 | ||
| Peak intensity | 60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min) | ||
On September 13, a tropical storm was first observed about 225 miles (360 km) southeast of Cape Hatteras, North Carolina.[3] A nearby ship with the call sign Cushnoc reported estimated winds of 60 mph (95 km/h), which was judged to be the peak intensity of the tropical storm. Another ship on September 16 reported similar winds in the same location;[10] Thus, it was estimated to have remained nearly stationary for three days. Its complete track is unknown.[3]
Tropical Storm Six
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | October 16 – October 19 | ||
| Peak intensity | 70 mph (110 km/h) (1-min) | ||
A tropical storm developed on October 16 about 155 miles (250 km) east of Cape Canaveral, Florida. It tracked northeastward, gradually strengthening to attain peak winds of 70 mph (110 km/h) early on October 17. On October 18, the storm turned more to the north-northeast as its forward motion increased. Gradually weakening, the storm dissipated late on October 19 after making landfall on Rhode Island.[3]
Other storms
On August 2, a hurricane was reported in the vicinity of Tampico.[11] However, it was not listed as a tropical cyclone in the official hurricane database.[1]
An assessment by scholar Michael Chenoweth indicated the presence of a hurricane in the vicinity of western Jamaica around November 7. It is not currently listed in the official hurricane database.[12]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 National Hurricane Center; Hurricane Research Division (July 6, 2016). "Atlantic hurricane best track (HURDAT version 2)". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved December 5, 2016.
- ↑ Chris Landsea (2007). "Counting Atlantic Tropical Cyclones Back to 1900" (PDF). American Meteorological Society. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 July 2007. Retrieved 2007-07-23.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Hurricane Research Division (2008). "Documentation of Atlantic Tropical Cyclones Changes in HURDAT". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 10 May 2008. Retrieved 2008-05-23.
- 1 2 3 New York Express (1851-09-12). "Great Storm in Florida, Alabama, and Georgia". Retrieved 2008-05-27.
- 1 2 3 Orlando Perez (1970). "Notes on the Tropical Cyclones of Puerto Rico" (PDF). National Weather Service. Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 May 2008. Retrieved 2008-05-27.
- ↑ Hurricane Research Division (2008). "Chronological List of All Hurricanes which Affected the Continental United States: 1851–2007" (TXT). Retrieved 2008-05-28.
- 1 2 New York Times (1852-01-01). "Principal Events of 1851" (PDF). The New York Times. Retrieved 2008-05-27.
- ↑ Al Sandrik & Chris Landsea (2003). "Chronological Listing of Tropical Cyclones affecting North Florida and Coastal Georgia 1565–1899". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 9 May 2008. Retrieved 2008-05-27.
- ↑ David M. Roth & Hugh Cobb (2001). "Virginia Hurricane History (1851–1900)". National Weather Service. Archived from the original on 9 May 2008. Retrieved 2008-05-27.
- ↑ Hurricane Research Division (2003). "Raw Observations for Tropical Storm Five in 1851" (XLS). Retrieved 2008-05-26.
- ↑ Milwaukee Daily Sentinel And Gazette (1851-08-23). "Telegraph by the O'Reilly Line". Retrieved 2008-05-23.
- ↑ Michael Chenoweth (2006). "A Reassessment of Historical Atlantic Basin Tropical Cyclone Activity, 1700–1855" (PDF). Hurricane Research Division. Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 May 2008. Retrieved 2008-05-25.