2,2,2-Trichlorethoxycarbonyl chloride
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,2,2-Trichlorethoxycarbonyl chloride | |
| Other names
Trichloroethyl chloroformate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 17341-93-4 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 78534 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.037.587 |
| PubChem | 10387 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H2Cl4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 211.85 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.539 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 0 °C (32 °F; 273 K) |
| Boiling point | 171 to 172 °C (340 to 342 °F; 444 to 445 K) |
| Hazards | |
| EU classification (DSD) |
Toxic (T), Corrosive (C) |
| R-phrases | R23, R34 |
| S-phrases | S26, S36/37/39 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Trichloroethyl chloroformate is used in organic synthesis for the introduction of the trichloroethyl chloroformate (Troc) protecting group for amines, thiols and alcohols. It readily cleaves vs other carbamates and can be used in an overall protecting group strategy.
The troc group is traditionally removed via Zn insertion in the presence of acetic acid, resulting in elimination and decarboxylation.
Amine Protection - 2,2,2-Trichloroethyl (Troc)
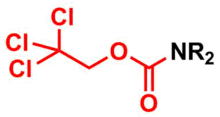
2,2,2-Trichloroethyl (Troc) group is largely used as a protecting group for amines in organic synthesis.
Most common amine protection methods
- 2,2,2-Trichloroethyl chloroformate, pyridine or aqueous sodium hydroxide at ambient temperature[2]

Most common amine deprotection method
References
- ↑ 2,2,2-Trichloroethyl chloroformate at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Marullo, N. P.; Wagener, E. H. (1969-01-01). "Structural organic chemistry by nmr. III. Isomerization of compounds containing the carbon-nitrogen double bond". Tetrahedron Letters. 10 (30): 2555–2558. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)88566-X.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/10/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
