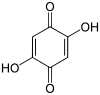
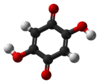
2,5-Dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,5-Dihydroxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione | |||
| Other names
2,5-Dihydroxy-p-benzoquinone, anilic acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 615-94-1 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image | ||
| ChemSpider | 62426 | ||
| PubChem | 69213 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H4O4 | |||
| Molar mass | 140.09 g·mol−1 | ||
| Melting point | 212.5 °C (414.5 °F; 485.6 K)[1] | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
2,5-Dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone or 2,5-dihydroxy-para-benzoquinone is an organic compound with formula C
6H
4O
4, formally derived from 1,4-benzoquinone by replacing two hydrogen atoms with hydroxyl (OH) groups. It is one of seven dihydroxybenzoquinone isomers. It is a yellow solid[1] with planar molecules[2] that exhibits ferroelectric properties.[3]
The compound is a weak acid: one or both hydroxyls can lose a proton to yield the anions C
6H
3O−
4 (pKa1 = 2.95) and C
6H
2O2−
4 (pKa2 = 4.87), respectively. The latter forms a variety of metal complexes, functioning as a binucleating ligand.[4]
The compound has been identified as partly responsible for the color of aged cellulosic materials.[5]
See also
References
- 1 2 Onkar Singh, Aran Kumar, and Karan Singh (2012), "Polymeric complexes of 2,5-Dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone with some Lanthanides". International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, volume 2, issue 9 ISSN 2250-3153
- ↑ Semmingsen, Dag "The crystal and molecular structure of 2,5-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone at -162°C" Acta Chemica Scandinavica, Series B: Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry 1977, volume B31, 11-14.
- ↑ Horiuchi, Sachio; Kumai, Reiji; Tokura, Yoshinori "Hydrogen-bonded donor-acceptor compounds for organic ferroelectric materials" Chemical Communications 2007, 2321-2329. doi:10.1039/B617881B
- ↑ Kitagawa, Susumu; Kawata, Satoshi "Coordination compounds of 1,4-dihydroxybenzoquinone and its homologues. Structures and properties" Coordination Chemistry Reviews 2002, volume 224, 11-34. doi:10.1016/S0010-8545(01)00369-1
- ↑ Hosoya, Takashi; French, Alfred D.; Rosenau, Thomas "Chemistry of 2,5-dihydroxy-[1,4]-benzoquinone, a key chromophore in aged cellulosics" Mini-Reviews in Organic Chemistry 2013, volume 10, pp. 309-315.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/14/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.