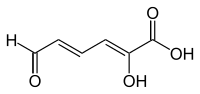
2-Hydroxymuconate semialdehyde
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
hydroxymuconic semialdehyde; 2-hydroxymuconate semialdehyde; 2-hydroxymuconate-6-semialdehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3270-98-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| PubChem | 5280366 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H6O4 | |
| Molar mass | 142.11 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2-Hydroxymuconate semialdehyde is formed from catechol by the enzyme catechol 2,3-dioxygenase during the degradation of benzoates.[1] It is hydrolysed into formate and 2-oxopent-4-enoate by 2-hydroxymuconate-semialdehyde hydrolase.
References
- ↑ Sala-Trepat JM, Evans WC (1971). "The meta cleavage of catechol by Azotobacter species 4-Oxalocrotonate pathway". Eur. J. Biochem. 20 (3): 400–13. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01406.x. PMID 4325686.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/7/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.