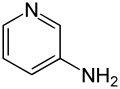
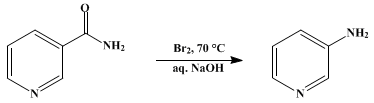3-Aminopyridine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Pyridin-3-amine | |
| Other names
3-Pyridinamine; 3-Pyridylamine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 462-08-8 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 9615 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.658 |
| PubChem | 10009 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H6N2 | |
| Molar mass | 94.12 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Dull brown crystals |
| Melting point | 65 °C (149 °F; 338 K) |
| Boiling point | 248 °C (478 °F; 521 K) |
| Soluble | |
| Solubility in alcohol and benzene | Soluble |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 124 °C (255 °F; 397 K) |
| 628 °C (1,162 °F; 901 K) | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
3-Aminopyridine is an aminopyridine. It can be used in the synthesis of organic ligand 3-pyridylnicotinamide
Preparation
3-Aminopyridine can be prepared by heating nicotinamide with sodium hypobromite which is in turn prepared in situ by the reaction of sodium hydroxide and bromine at 70 °C.[1]
Toxicology
3-Aminopyridine can easily be absorbed through the skin. It is fatal if swallowed or absorbed through the skin. High concentrations can be extremely destructive to the tissues of mucous membranes and upper respiratory tract eyes and skin. Symptoms may also include convulsions and death. It also causes damage to the nervous system. Thermal decomposition leads to evolution of toxic gases such as carbon monoxide and oxides of nitrogen.
References
- ↑ C. F. H. Allen and Calvin N. Wolf (1950). "3-Aminopyridine". Org. Synth. 30: 3.; Coll. Vol., 4, p. 45
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 3/16/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.