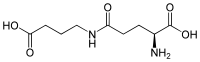
4-(γ-Glutamylamino)butanoic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Amino-5-[(4-hydroxy-4-oxobutyl)amino]-5-oxopentanoic acid | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
4-Amino-5-((3-carboxypropyl)amino)-5-oxopentanoic acid | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| 5105-96-4 S | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| Abbreviations |
|
| 2418119 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:49260 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL269574 |
| ChemSpider | 315618 |
| KEGG | C15767 |
| PubChem | 355553 23724570 S |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H16N2O5 | |
| Molar mass | 232.24 g·mol−1 |
| log P | −1.434 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.223 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 11.777 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related alkanoic acids |
|
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
4-(γ-Glutamylamino)butanoic acid is molecule that consists of L-glutamate conjugated to γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). It is the substrate of the enzyme γ-glutamyl-γ-aminobutyrate hydrolase, which is involved in the biosynthesis of polyamines.[2]
References
- ↑ "NSC609423 - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification. Retrieved 8 July 2012.
- ↑ Kurihara S, Oda S, Kato K, Kim HG, Koyanagi T, Kumagai H, Suzuki H (2005). "A novel putrescine utilization pathway involves gamma-glutamylated intermediates of Escherichia coli K-12". J. Biol. Chem. 280: 4602–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M411114200. PMID 15590624.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/17/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.