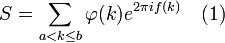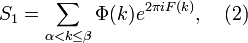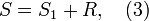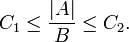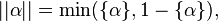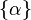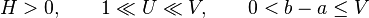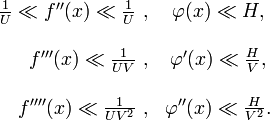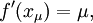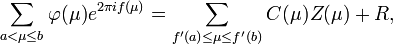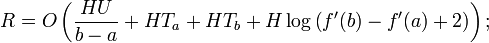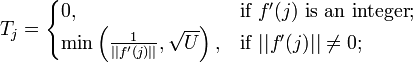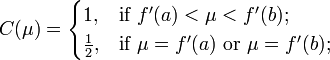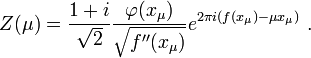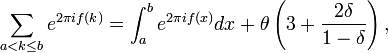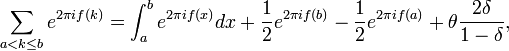ATS theorem
In mathematics, the ATS theorem is the theorem on the approximation of a trigonometric sum by a shorter one. The application of the ATS theorem in certain problems of mathematical and theoretical physics can be very helpful.
History of the problem
In some fields of mathematics and mathematical physics, sums of the form
are under study.
Here 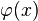 and
and 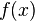 are real valued functions of a real
argument, and
are real valued functions of a real
argument, and  Such sums appear, for example, in number theory in the analysis of the
Riemann zeta function, in the solution of problems connected with
integer points in the domains on plane and in space, in the study of the
Fourier series, and in the solution of such differential equations as the wave equation, the potential equation, the heat conductivity equation.
Such sums appear, for example, in number theory in the analysis of the
Riemann zeta function, in the solution of problems connected with
integer points in the domains on plane and in space, in the study of the
Fourier series, and in the solution of such differential equations as the wave equation, the potential equation, the heat conductivity equation.
The problem of approximation of the series (1) by a suitable function was studied already by Euler and Poisson.
We shall define
the length of the sum 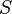 to be the number
to be the number 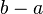 (for the integers
(for the integers 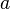 and
and 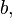 this is the number of the summands in
this is the number of the summands in 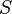 ).
).
Under certain conditions on 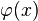 and
and 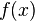 the sum
the sum 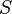 can be
substituted with good accuracy by another sum
can be
substituted with good accuracy by another sum 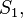
where the length 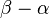 is far less than
is far less than 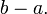
First relations of the form
where 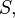
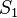 are the sums (1) and (2) respectively,
are the sums (1) and (2) respectively, 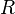 is
a remainder term, with concrete functions
is
a remainder term, with concrete functions 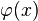 and
and 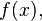 were obtained by G. H. Hardy and J. E. Littlewood,[1][2][3]
when they
deduced approximate functional equation for the Riemann zeta function
were obtained by G. H. Hardy and J. E. Littlewood,[1][2][3]
when they
deduced approximate functional equation for the Riemann zeta function
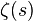 and by I. M. Vinogradov,[4] in the study of
the amounts of integer points in the domains on plane.
In general form the theorem
was proved by J. Van der Corput,[5][6] (on the recent
results connected with the Van der Corput theorem one can read at
[7]).
and by I. M. Vinogradov,[4] in the study of
the amounts of integer points in the domains on plane.
In general form the theorem
was proved by J. Van der Corput,[5][6] (on the recent
results connected with the Van der Corput theorem one can read at
[7]).
In every one of the above-mentioned works,
some restrictions on the functions
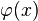 and
and 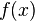 were imposed. With
convenient (for applications) restrictions on
were imposed. With
convenient (for applications) restrictions on
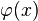 and
and 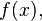 the theorem was proved by A. A. Karatsuba in [8] (see also,[9][10]).
the theorem was proved by A. A. Karatsuba in [8] (see also,[9][10]).
Certain notations
[1]. For 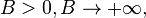 or
or 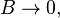 the record
the record
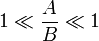 means that there are the constants
means that there are the constants  and
and 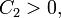 such that
such that
[2]. For a real number 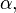 the record
the record
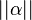 means that
means that
where
is the fractional part of 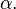
ATS theorem
Let the real functions ƒ(x) and 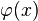 satisfy on the segment [a, b] the following conditions:
satisfy on the segment [a, b] the following conditions:
1) 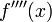 and
and 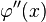 are continuous;
are continuous;
2) there exist numbers
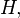
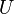 and
and 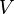 such that
such that
- and
Then, if we define the numbers 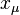 from the equation
from the equation
we have
where
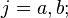
The most simple variant of the formulated theorem is the statement, which is called in the literature the Van der Corput lemma.
Van der Corput lemma
Let 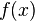 be a real differentiable function in the interval
be a real differentiable function in the interval
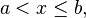 moreover, inside of this interval, its derivative
moreover, inside of this interval, its derivative
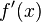 is a monotonic and a sign-preserving function, and for the constant
is a monotonic and a sign-preserving function, and for the constant 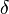 such that
such that 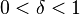 satisfies the inequality
satisfies the inequality
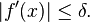 Then
Then
where 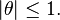
Remark
If the parameters 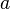 and
and 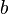 are integers, then it is possible to substitute the last relation by the following ones:
are integers, then it is possible to substitute the last relation by the following ones:
where 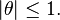
On the applications of ATS to the problems of physics see,;[11][12] see also,.[13][14]
Notes
- ↑ G.~H. Hardy and J.~E. Littlewood. The trigonometrical series associated with the elliptic $\theta$-functions. Acta Math. 37, pp. 193—239 (1914).
- ↑ G.~H. Hardy and J.~E. Littlewood. Contributions to the theory of Riemann Zeta-Function and the theory of the distribution of primes. Acta Math. 41, pp. 119—196 (1918).
- ↑ G.~H. Hardy and J.~E. Littlewood. The zeros of Riemann's zeta-function on the critical line, Math. Z., 10, pp. 283–317 (1921).
- ↑ I.~M. Vinogradov. On the average value of the number of classes of purely root form of the negative determinant Communic. of Khar. Math. Soc., 16, 10–38 (1917).
- ↑ J.~G. Van der Corput. Zahlentheoretische Abschätzungen. Math. Ann. 84, pp. 53–79 (1921).
- ↑ J.~G. Van der Corput. Verschärfung der Abschätzung beim Teilerproblem. Math. Ann., 87, pp. 39–65 (1922).
- ↑ H.~L. Montgomery. Ten Lectures on the Interface Between Analytic Number Theory and Harmonic Analysis, Am. Math. Soc., 1994.
- ↑ A.~A. Karatsuba. Approximation of exponential sums by shorter ones. Proc. Indian. Acad. Sci. (Math. Sci.) 97: 1–3, pp. 167—178 (1987).
- ↑ A.~A. Karatsuba, S. M. Voronin. The Riemann Zeta-Function. (W. de Gruyter, Verlag: Berlin, 1992).
- ↑ A.~A. Karatsuba, M. A. Korolev. The theorem on the approximation of a trigonometric sum by a shorter one. Izv. Ross. Akad. Nauk, Ser. Mat. 71:3, pp. 63—84 (2007).
- ↑ E.~A. Karatsuba. Approximation of sums of oscillating summands in certain physical problems. JMP 45:11, pp. 4310—4321 (2004).
- ↑ E.~A. Karatsuba. On an approach to the study of the Jaynes–Cummings sum in quantum optics, Numerical Algorithms, Vol. 45, No. 1–4 , pp. 127–137 (2007).
- ↑ E. Chassande-Mottin, A. Pai. Best chirplet chain: near-optimal detection of gravitational wave chirps. Phys. Rev. D 73:4, 042003, pp. 1—23 (2006).
- ↑ M. Fleischhauer, W.~P. Schleich. Revivals made simple: Poisson summation formula as a key to the revivals in the Jaynes-Cummings model. Phys. Rev. A 47:3, pp. 4258—4269 (1993).