Ancient Agora of Athens
| Αρχαία Αγορά της Αθήνας | |
 Central Athens | |
| Alternate name | Forum of Athens |
|---|---|
| Location | Greece |
| Region | Attica |
| Coordinates | 37°58′30″N 23°43′21″E / 37.97500°N 23.72250°E |
| History | |
| Material | Marble |
| Founded | 6th century BC |
| Periods | Classical era |
| Cultures | Ancient Greece |
| Site notes | |
| Excavation dates | 1931 until today |
| Archaeologists | American School of Classical Studies at Athens |
| Condition | Ruined |
| Ownership | Public property |
| Management | Minister for Culture |
| Public access | Yes |

The Ancient Agora of Classical Athens is the best-known example of an ancient Greek agora, located to the northwest of the Acropolis and bounded on the south by the hill of the Areopagus and on the west by the hill known as the Agoraios Kolonos, also called Market Hill.[1]
Buildings and structures of the classical agora
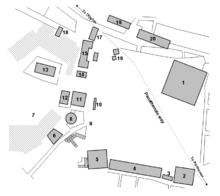
- Peristyle Court
- Mint
- Enneakrounos
- South Stoa I and South Stoa II
- Aiakeion
- Strategeion
- Agoraios Kolonos
- Tholos
- Agora stone
- Monument of the Eponymous Heroes
- Metroon (Old Bouleuterion)
- New Bouleuterion
- Temple of Hephaestus (Hephaestion)
- Temple of Apollo Patroos
- Stoa of Zeus
- Altar of the Twelve Gods
- Stoa Basileios (Royal stoa)
- Temple of Aphrodite Urania
- Stoa of Hermes
- Stoa Poikile
Other notable monuments

A number of other notable monuments were added to the agora. Some of these included:
- The Middle stoa which was the most extensive monument built during the 100s B.C.E.[2]
- A small Roman temple was added in front of the Middle stoa.
- An Altar of Zeus Agoraios was added just to the east of the Monument to the Eponymous Heroes.[3]
- The Temple of Ares, dedicated to Ares, the god of war, was added in the north half agora, just south of the Altar of the Twelve Gods.[4]
- The Odeon of Agrippa and accompanying gymnasium were added in the centre of the agora.[5]
- The substantial Stoa of Attalos was built along the eastern edge of the agora.[6]
- A collection of buildings were added to the south-east corner: the East stoa, the Library of Pantainos, the Nymphaeum and a temple.
- There is evidence of a Synagogue in the Agora of Athens in the 3rd century.
- A statue of the Roman emperor Hadrian was located near the metroon.[7]
- The Temple of Zeus Phratrios and Athena Phratria dated to the 300s B.C.E. and is located near the Temple of Apollo Patroos.[8]
- The south end of what is believed to be a Basilica has been uncovered near Hadrian Street and is dated to the mid 100s C.E.[9]
- The Monopteros was located south of the Basilica and also dated to the mid 100s C.E. It had no walls, was a dome supported by columns and was about 8 meters in diameter.[10]
- The Bema was a speakers platform and was located near the Stoa of Attalos.[11]
Excavations
The ancient Athenian agora has been excavated by the American School of Classical Studies at Athens since 1931 under the direction of T. Leslie Shear, Sr. They continue to the present day, now under the direction of John McK Camp.
After the initial phase of excavation, in the 1950s, the Hellenistic Stoa of Attalos was reconstructed on the east side of the agora, and today it serves as a museum and as storage and office space for the excavation team.
A virtual reconstruction of the Ancient Agora of Athens has been produced through a collaboration of the American School of Classical Studies at Athens and the Foundation of the Hellenic World, which had various output (3d video, VR real-time dom performance, Google Earth 3d models).[12]
Museum of the Ancient Agora
The museum is housed in the Stoa of Attalos, and its exhibits are connected with the Athenian democracy. The collection of the museum includes clay, bronze and glass objects, sculptures, coins and inscriptions from the 7th to the 5th century BC, as well as pottery of the Byzantine period and the Turkish occupation.
See also
References
- ↑ R. E. Wycherley, Literary and Epigraphical Testimonia (Athenian Agora) (American School of Classical Studies, 1957), pg. 27.
- ↑ Camp, The Athenian Agora: Site Guide, pg. 168.
- ↑ Camp, The Athenian Agora: Site Guide, pg. 65.
- ↑ Camp, The Athenian Agora: Site Guide, pg. 110.
- ↑ Camp, The Athenian Agora: Site Guide, pg. 114.
- ↑ Camp, The Athenian Agora: Site Guide, pg. 123.
- ↑ Camp, The Athenian Agora: Site Guide, pg. 63.
- ↑ Camp, The Athenian Agora: Site Guide, pg. 73.
- ↑ Camp, The Athenian Agora: Site Guide, pg. 93.
- ↑ Camp, The Athenian Agora: Site Guide, pg. 118.
- ↑ Camp, The Athenian Agora: Site Guide, pg. 122.
- ↑ Sideris A., "A Virtual Cradle for Democracy: Reconstructing the Ancient Agora of Athens", Proceedings of the International SEEArchWeb Conference, Thessaloniki, September 2006.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ancient Agora of Athens. |
- Hellenic Ministry of Culture: The Ancient Agora of Athens – official site with a schedule of its opening hours, tickets and contact information.
- Agora Excavations – American School of Classical Studies Agora excavation project.
- Map of the Agora of Athens in Socrates and Plato's time
- Agora of Athens in 421 BC
- The Athenian Agora: A Short Guide in Color
- The Athenian Agora. A Guide to the Excavation and Museum
- Reconstruction of the Athenian Agora in Google Earth
- Ministry of Culture: The Museum
- www.athensinfoguide.com The Museum
- Agora of Athens: photo album and description
- Agora of Athens photos
Coordinates: 37°58′30″N 23°43′21″E / 37.97500°N 23.72250°E