Annonaceae
| Annonaceae | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Annona squamosa fruit | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Magnoliids |
| Order: | Magnoliales |
| Family: | Annonaceae Juss. |
| Genera | |
|
See text | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Hornschuchiaceae J. Agardh | |
The Annonaceae are a family, the custard apple family,[2][3] of flowering plants consisting of trees, shrubs, or rarely lianas.[3] With 108 accepted genera and about 2400 known species,[4] it is the largest family in the Magnoliales. Several genera produce edible fruit, most notably Annona, Anonidium, Asimina, Rollinia, and Uvaria. Its type genus is Annona. The family is concentrated in the tropics, with few species found in temperate regions. About 900 species are Neotropical, 450 are Afrotropical, and the other species Indomalayan.
Description
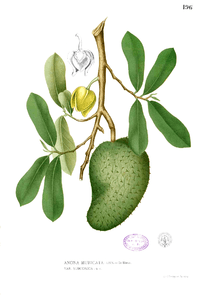
The species are mostly tropical, some are mid-latitude, deciduous or evergreen trees and shrubs, with some lianas, with aromatic bark, leaves, and flowers.[3]
- Stems, stalks and leaves
- Bark is fibrous and aromatic. Pith septate (fine tangential bands[5] divided by partitions) to diaphragmed (divided by thin partitions with openings in them).[3] Branching distichous (arranged in two rows/on one plane) or spiral.[6] Leaves are alternate, two-ranked,[6] simple, pinnately veined, and have leaf stalks. Stipules absent.[3]
- Flowers
- Flower stalks are axillary to (on the opposite side of shoot from) leaf scars on old wood and sometimes from leaves on new shoots. The flowers are usually trimerous; borne singly or in compound inflorescences; bisexual and rarely unisexual. The receptacle might become enlarged, elevated or flat. The outer whorls are inserted below the ovaries, and have valvate (overlapping) or imbricate (nonoverlapping) segments. Usually two to four persistent sepals that are distinct or connate (fused) at the base. Six petals in two unequal whorls of three with larger outer whorls and fleshier inner whorls that might share the same nectar glands, or six to fifteen petals, with impressed veins on their inner face. Ten to twenty (or many more) stamens inserted below the ovary, spirally arranged and forming a ball or flat-topped mass with short and stout filaments and linear to oblong anthers which face outward and open longitudinally. Each flower can have from one to many pistils, distinct to connate, with stigmas distinct. Marginal placentation, each pistil bearing one locule, with one to many ovules. Style short and thick, with terminal stigma.[3]
- Fruits and seeds
- Fruits are single berries or coalesce from several pistils (into aggregate fruit, syncarps). Seeds are one to many per pistil; have a fleshy and usually brightly colored cover, have ruminate endosperm (nutritive tissue surrounding the embryo) and are oily.[3]
Systematics
Monophyly and inter-familial systematics have been well supported for Annonaceae by a combination of morphological and molecular evidence.[7] The APG II system places Annonaceae as most closely related to the small Magnoliid family Eupomatiaceae.
|
In a phylogeny-based reclassification of the family [4] four subfamilies are recognised: Anaxagoreoideae (including just Anaxagorea), Ambavioideae, Annonoideae, and Malmeoideae. A number of the larger genera, including Guatteria, with its 177 species,[8] Annona, and Xylopia belong to Annonoideae. Together, Annonoideae and Malmeoideae comprise the majority of the species and each are further subdivided into a number of tribes. The subfamilial and tribal classification is followed in World Annonaceae which presents an overview of all Annonaceae genera and taxonomic, distribution and photographic information for a large number of species. Keys for the identification of Annonaceae genera (separately for Neotropical, African/Madagascan, and Asian/Australian taxa) are presented in [9] . For a concise bibliographic overview of the taxonomic literature (1900 to 2012) see.[10]
Both plastid DNA markers and morphological characters provide evidence that Anaxagorea is the sister clade to the rest of the family. This may confirm the hypothesis that morphological traits shared between Anaxagorea and other Magnoliales species (such as 2-ranked phyllotaxis, monosulcate pollen, and laminate stamens) represent ancestral characters, while derived characters observed in other genera have evolved independently multiple times.[11][12][13] The oldest fossil evidence of Annonaceae is described as the genus Futabanthus, from the late Cretaceous of Japan,[14] which represents a minimum age of c. 89 Mya for the most recent common ancestor (crown group) of the family.[15] The ages of Annonaceae clades inferred using fossil evidence and molecular clock based dating techniques suggests that the pantropical distribution of the family originated subsequent to the break up of the Gondwanan supercontinent, as the result of a combination of geodispersal tracking the expansion of the boreotropical flora during the Eocene and more recent long distance dispersal events.[16][17]
Uses

Food
The large, edible, pulpy fruits of some members typically called anona by Spanish- and Portuguese-speaking people of the family's Neotropical range, include species of Annona: custard apple (A. reticulata), cherimoya (A. cherimola), soursop/guanábana/graviola (A. muricata), sweetsop (A. squamosa), ilama (A. diversifolia), soncoya (A. purpurea), atemoya (a cross between A. cherimola and A. squamosa); and biriba (Rollinia deliciosa, which may require reclassification under Annona.[18]). The names of many of those fruits are sometimes used interchangeably. Recently, consumption of the neotropical annonaceous plant Annona muricata (soursop, graviola, guanabana) has been strongly associated as a causal agent in "atypical Parkinsonism". The causative agent, annonacin, is present in many of the Annonaceae. It is thought to be responsible for up to 70% of Parkinsonian conditions in Guadeloupe. Exposure is typically through traditional food and natural medicines.[19][20][21][22]
Asimina triloba (American pawpaw, prairie banana) has an Eastern U.S. distribution, and is currently under investigation as a commercial agricultural crop.[23]
Folk medicine
The bark, leaves, and roots of some species are used in folk medicines.
Toxicology
The compound annonacin in the seeds and leaves of many Annonaceae including Annona muricata (soursop), is a neurotoxin and it seems to be the cause of a neurodegenerative disease. The disorder is a so-called tauopathy associated with a pathologic accumulation of tau protein in the brain. Experimental results demonstrate that the plant neurotoxin annonacin is responsible for this accumulation.[24]
Other uses
Lancewood (Oxandra lanceolata)[25] is a tough, elastic, and heavy wood obtained from the West Indies and The Guianas. It was often used for carriage shafts. It is brought into commerce in the form of taper poles of about 6 m in length and from 15 to 20 cm in breadth at the butt. The black lancewood or carisiri of The Guianas is of remarkably slender form.
The yellow lancewood tree Calycophyllum candididissimum, common names lemonwood or degame, is from a different family (Rubiaceae).[25] It is used as an alternative to lancewood and is found in tolerable abundance throughout The Guianas, and used by the Amerinds for arrow-points, as well as for spars, beams, etc. Some bowyers use this wood for making longbows.
Other

- Some species of the family, such as Cananga odorata (ylang-ylang) also have aromatic oil and are used for perfumes or spices.[5]
- The strong bark is used for carrying burdens in the Amazon Rainforest[5] and for wooden implements, such as tool handles and pegs.[26] The wood is valued as firewood.[5]
- Yellow and brown dyes[26]
- Some species are also grown as ornamental plants, especially the Indian species Polyalthia longifolia pendula.
- The fruit and leaves of Uvariopsis tripetala (pepperfruit) are used as a spice for meats in some parts of Nigeria, due to its "hot" peppery flavor.
Chemical constituents
A large number of chemical compounds, including flavonoids, alkaloids, and acetogenins, have been extracted from the seeds and many other parts of these plants. Flavonoids and alkaloids contained in the leaves and bark of several species of the family have shown insecticidal properties.[26]
Genera
- Afroguatteria
- Alphonsea
- Ambavia
- Anaxagorea
- Ancana
- Annickia
- Annona
- Anomianthus
- †Anonaspermum[27]
- Anonidium
- Artabotrys—trail-grape
- Asimina
- Asteranthe
- Balonga
- Bocagea
- Bocageopsis
- Boutiquea
- Cananga—Ylang-ylang
- Cardiopetalum
- Cleistochlamys
- Cleistopholis
- Craibella
- Cremastosperma
- Cyathocalyx
- Cyathostemma
- Cymbopetalum
- Dasoclema
- Dasymaschalon
- Deeringothamnus—false pawpaw
- Dendrokingstonia
- Dennettia
- Desmopsis
- Desmos
- Diclinanona
- Dielsiothamnus
- Disepalum
- Duckeanthus
- Duguetia
- Ellipeia
- Ellipeiopsis
- Enicosanthum
- Ephedranthus
- Exellia
- Fissistigma
- Fitzalania
- Friesodielsia
- Froesiodendron
- Fusaea
- Gilbertiella
- Goniothalamus
- Greenwayodendron
- Guamia
- Guatteria—haya minga, haya blanca
- Guatteriella
- Guatteriopsis
- Haplostichanthus
- Heteropetalum
- Hexalobus
- Hornschuchia
- Isolona
- Letestudoxa
- Lettowianthus
- Malmea
- Marsypopetalum
- Meiocarpidium
- Meiogyne
- Melodorum
- Mezzettia
- Mezzettiopsis
- Miliusa
- Mischogyne
- Mitrella
- Mitrephora
- Mkilua
- Monanthotaxis
- Monocarpia
- Monocyclanthus
- Monodora
- Mosannona
- Neostenanthera
- Neo-uvaria
- Onychopetalum
- Ophrypetalum
- Oreomitra
- Orophea
- Oxandra—blacklancewood, vernacular name: haya
- Pachypodanthium
- Papualthia
- Petalolophus
- Phaeanthus
- Phoenicanthus
- Piptostigma
- Platymitra
- Polyalthia
- Polyceratocarpus
- Popowia
- Porcelia
- Pseudartabotrys
- Pseudephedranthus
- Pseudoxandra
- Pseuduvaria
- Pyramidanthe
- Raimondia
- Reedrollinsia
- Richella
- Rollinia—wild sugar-apple
- Ruizodendron
- Sageraea
- Sanrafaelia
- Sapranthus
- Schefferomitra
- Sirdavidia
- Sphaerocoryne
- Stelechocarpus—kepel
- Stenanona
- Tetrameranthus
- Toussaintia
- Tridimeris
- Trigynaea
- Trivalvaria
- Unonopsis
- Uvaria
- Uvariastrum
- Uvariodendron
- Uvariopsis
- Woodiellantha
- Xylopia
References
- ↑ Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN) (2007-05-12). "Family: Annonaceae Juss., nom. cons.". Taxonomy for Plants. USDA, ARS, National Genetic Resources Program, National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. Retrieved 2008-04-18.
- ↑ "Annonaceae". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 18 March 2008.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Flora of North America. "2. Annonaceae Jussieu". 3. Archived from the original on 21 April 2008. Retrieved 2008-04-20.
- 1 2 Chatrou, L. W.; M. D. Pirie; R. H. J. Erkens; T. L. P. Couvreur; K. M. Neubig; J. R. Abbott; J. B. Mols; P. J. M. Maas; R. M. K. Saunders; Mark W. Chase (2012). "A new subfamilial and tribal classification of the pantropical flowering plant family Annonaceae informed by molecular phylogenetics". Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society. 169: S. 4–50. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8339.2012.01235.x.
- 1 2 3 4 Chatrou, Dr. L.W. (2005-07-29). "Molecular Systematics of Annonaceae". Annonaceae research projects. Nationaal Herbarium Nederland. Archived from the original on 2008-01-13. Retrieved 2008-04-20.
- 1 2 Johnson, D.M. (July–September 2003). "Phylogenetic significance of spiral and distichous architecture in the Annonaceae.". Systematic Botany. 28 (3): 503–511. doi:10.1043/02-13.1.
- ↑ Doyle, J.A.; H. Sauquet; T. Scharaschkin (2004). "Phylogeny, molecular and fossil dating, and biogeographic history of Annonaceae and Myristicaceae (Magnoliales)". International Journal of Plant Sciences. 165 (4): 55–67. doi:10.1086/421068.
- ↑ Maas, P.J.M.; Westra, L.Y.T.; Guerrero, S. Arias; Lobão, A.Q.; Scharf, U.; Zamora, N.A.; Erkens, R.H.J. (2015). "Confronting a morphological nightmare: revision of the Neotropical genus Guatteria (Annonaceae)". Blumea - Biodiversity, Evolution and Biogeography of Plants. 60 (1): 1–219. doi:10.3767/000651915X690341. ISSN 0006-5196.
- ↑ Couvreur, Thomas L. P.; Maas, Paul J. M.; Meinke, Svenja; Johnson, David M.; KEßLER, PAUL J. A. (2012). "Keys to the genera of Annonaceae". Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society. 169 (1): 74–83. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8339.2012.01230.x. ISSN 0024-4074.
- ↑ Erkens, Roy H. J.; Mennega, Erik A.; Westra, Lubbert Y. Th. (2012). "A concise bibliographic overview of Annonaceae". Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society. 169 (1): 41–73. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8339.2012.01232.x. ISSN 0024-4074.
- ↑ Scharaschkin, T.; J.A. Doyle (2005). "Phylogeny and historical biogeography of Anaxagorea (Annonaceae) using morphology and non-coding chloroplast sequence data.". Systematic Botany. 30 (5): 712–735. doi:10.1600/036364405775097888.
- ↑ Scharaschkin, T.; J.A. Doyle (2006). "Character evolution in Anaxagorea (Annonaceae)". American Journal of Botany. 93 (1): 36–54. doi:10.3732/ajb.93.1.36.
- ↑ Doyle, James A.; Le Thomas, Annick (2012). "Evolution and phylogenetic significance of pollen in Annonaceae". Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society. 169 (1): 190–221. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8339.2012.01241.x. ISSN 0024-4074.
- ↑ Takahashi, Masamichi; Friis, Else Marie; Uesugi, Kentaro; Suzuki, Yoshio; Crane, Peter R. (2008). "Floral Evidence of Annonaceae from the Late Cretaceous of Japan". International Journal of Plant Sciences. 169 (7): 908–917. doi:10.1086/589693. ISSN 1058-5893.
- ↑ Pirie, Michael D.; Doyle, James A. (2012). "Dating clades with fossils and molecules: the case of Annonaceae". Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society. 169 (1): 84–116. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8339.2012.01234.x. ISSN 0024-4074.
- ↑ Richardson, J. E.; Chatrou, L. W.; Mols, J. B.; Erkens, R. H. J.; Pirie, M. D. (2004). "Historical biogeography of two cosmopolitan families of flowering plants: Annonaceae and Rhamnaceae". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 359 (1450): 1495–1508. doi:10.1098/rstb.2004.1537. ISSN 0962-8436.
- ↑ Couvreur, Thomas L. P.; Pirie, Michael D.; Chatrou, Lars W.; Saunders, Richard M. K.; Su, Yvonne C. F.; Richardson, James E.; Erkens, Roy H. J. (2011). "Early evolutionary history of the flowering plant family Annonaceae: steady diversification and boreotropical geodispersal". Journal of Biogeography. 38 (4): 664–680. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2699.2010.02434.x. ISSN 0305-0270.
- ↑ Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN) (2008-02-14). "Genus: Rollinia A. St.-Hil.". Taxonomy for Plants. USDA, ARS, National Genetic Resources Program, National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. Retrieved 2008-04-16.
- ↑ Lannuzel, A; et al. (2003-10-06). "The mitochondrial complex i inhibitor annonacin is toxic to mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons by impairment of energy metabolism". Neuroscience. International Brain Research Organization. 121 (2): 287–296. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(03)00441-X. PMID 14521988.
- ↑ Champy, Pierre; et al. (2005-08-02). "Quantification of acetogenins in Annona muricata linked to atypical parkinsonism in guadeloupe". Movement Disorders. 20 (12): 1629–1633. doi:10.1002/mds.20632. PMID 16078200.
- ↑ Lannuzel A, Höglinger GU, Champy P, Michel PP, Hirsch EC, Ruberg M (2006). "Is atypical parkinsonism in the Caribbean caused by the consumption of Annonacae?". J Neural Transm Suppl. Journal of Neural Transmission. Supplementa. 70 (70): 153–7. doi:10.1007/978-3-211-45295-0_24. ISBN 978-3-211-28927-3. PMID 17017523.
- ↑ Caparros-Lefebvre D, Elbaz A (1999-07-24). "Possible relation of atypical parkinsonism in the French West Indies with consumption of tropical plants: a case-control study". Lancet. 354 (9175): 281–6. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(98)10166-6. PMID 10440304.
- ↑ Pomper, K.W.; et al. (July 2008). "Flowering and fruiting characteristics of eight pawpaw [Asimina triloba (L.)] Dunal selections in Kentucky". Journal American Pomological Society. 62 (3): 89–97.
- ↑ Informationsdienst Wissenschaft: Tauopathie durch pflanzliches Nervengift Archived June 13, 2007, at the Wayback Machine., 4. Mai 2007
- 1 2 Lincoln, William A (1986). World Woods in Colour. Hertford UK: Stobard Davies Ltd. ISBN 0-85442-028-2.
- 1 2 3 University of Southampton (March 2002). "Factsheet No. 5. Annona" (PDF). Fruits for the Future. Department for International Development, International Centre for Underutilised Crops. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-20. Retrieved 2008-04-20.
- ↑ Manchester, S.R. (1994). "Fruits and Seeds of the Middle Eocene Nut Beds Flora, Clarno Formation, Oregon". Palaeontographica Americana. 58: 30–31.
-
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Custard Apple". Encyclopædia Britannica. 7 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 667.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Custard Apple". Encyclopædia Britannica. 7 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 667.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Annonaceae. |
| Wikispecies has information related to: Annonaceae |
- "Annonaceae". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 18 March 2008.
- AnnonBase—online database for Annonaceae
- World Annonaceae - a scratchpad for data on species of Annonaceae