Azerizin
Azerizin is claimed to be a proprietary blend of the natural ingredients nicotinamide, azelaic acid, quercetin and curcumin that purportedly combine the anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, along with inhibiting effects on sebum production.
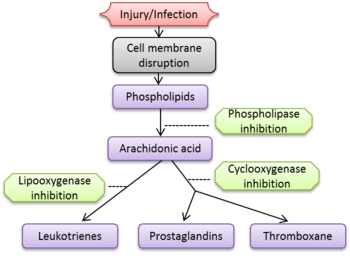
The cascade of events in the inflammatory pathway that result from cell membrane disruption is well documented.[1][2] The release of membrane phospholipids leads to increased production of arachidonic acid which in turn results in elevated leukotriene, prostaglandin and thromboxane production. The ingredients in Azerizin are known to inhibit each of these three major paths of inflammation by blocking or down-regulating pro-inflammatory catalysts at multiple points in the inflammatory cascade, e.g., inhibition of phospholipase, lipooxygenase, COX-2, leukotrienes, thromboxane, prostaglandins, nitric oxide, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin-12.[3][4][5][6]
In addition to these anti-inflammatory actions, the components of Azerizin possess potent antimicrobial activity against Propionibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidermis, at least in part attributed to inhibition of microbial cellular protein synthesis.[7][8][9] Azerizin was developed at Elorac for use as an adjunct in the management of acne vulgaris and rosacea.
References
- ↑ Herskowitz, Ahvie; Mangano, Dennis T. (November 1996). "Inflammatory Cascade: A Final Common Pathway for Perioperative Injury?". Anesthesiology. 85 (5): 957–960. doi:10.1097/00000542-199611000-00001.
- ↑ Chainani-wu, Nita (2003). "Safety and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Curcumin: A Component of Tumeric {sic} (Curcuma longa)" (PDF). The Journal of Alternate and Complementary Medicine. 9: 161–168. doi:10.1089/107555303321223035. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-10-14.
- ↑ Chirumbolo, S (Sep 2010). "The role of quercetin, flavonols and flavones in modulating inflammatory cell function". Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 9 (4): 263–85. doi:10.2174/187152810793358741. PMID 20887269.
- ↑ Fivenson, DP (Jan 2006). "The mechanisms of action of nicotinamide and zinc in inflammatory skin disease". Cutis (1 Suppl): 5–10.
- ↑ Jurenka, Julie S (2 Nov 2009). "Anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin, a major constituent of Curcuma longa: A review of preclinical and clinical research". Alternative Medicine Review. 14 (f2): 141–153.
- ↑ Shalita, A; Falcon R; Olansky A; Oannotta P; Akhavan A; Day D; Janiga A; Singri P; Kallal J (2012). "Inflammatory acne management with a novel prescription dietary supplement". Journal of Drugs in Dermatology. 11.
- ↑ Liu, C; Huang H (2013). "In Vitro Anti-Propionibacterium Activity by Curcumin Containing Vesicle System". Chem Pharm Bull. 61 (4): 419–425. doi:10.1248/cpb.c12-01043. PMID 23546001.
- ↑ "azelaic acid - Compound Summary". PubChem.
- ↑ Fitton, Andrew; Goa, Karen L (1991). "Azelaic acid: A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in acne and hyperpigmentary skin disorders". Drugs. 41 (5): 780–798. doi:10.2165/00003495-199141050-00007. PMID 1712709.
External links
- Evidence-based information about herbs, botanicals, supplements, and more, from Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine Guide, from the University of Maryland Medical Center
- Management Options for Rosacea, from the National Rosacea Society
- Complementary and Alternative Therapies, from the National Psoriasis Foundation