Azinphos-ethyl
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
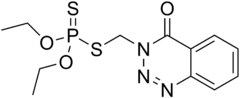
| IUPAC name
3-(Diethoxyphosphinothioylsulfanylmethyl)-1,2,3-benzotriazin-4-one | |
| Other names
Gusathion; Ethyl azinphos | |
| Identifiers | |
| 2642-71-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:38587 |
| ChemSpider | 16576 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.018.316 |
| KEGG | C18644 |
| PubChem | 17531 |
| RTECS number | TD8400000 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H16N3O3PS2 | |
| Molar mass | 345.37 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals |
| Melting point | 53 °C (127 °F; 326 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
17.5 mg/kg (oral, rat)[1] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Azinphos-ethyl (also spelled azinophos-ethyl) is a broad-spectrum organophosphate insecticide.
Regulation
It is very toxic to mammals with a World Health Organization hazard classification as class IB, highly hazardous.[2] It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (42 U.S.C. 11002), and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.[3]
See also
References
- 1 2 Azinphos-Ethyl, Chemical Sampling Information, Occupational Safety and Health Administration
- ↑ Azinphos-ethyl Pesticide Data Sheet Archived June 8, 2011, at the Wayback Machine., International Programme on Chemical Safety
- ↑ "40 C.F.R.: Appendix A to Part 355—The List of Extremely Hazardous Substances and Their Threshold Planning Quantities" (PDF) (July 1, 2008 ed.). Government Printing Office. Retrieved October 29, 2011.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/19/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.