Azoxy

The structure of the azoxy functional group, where R is a substituent.
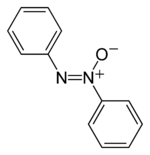
Azoxybenzene - An example azoxy compound.
Azoxy compounds are a group of chemical compounds sharing a common functional group with the general structure RN=N+(O−)R.[1] They are considered N-oxides of azo compounds. Azoxy compounds are 1,3-dipoles. They undergo 1,3 dipolar cycloaddition with double bonds.
Preparation
Most azoxy-containing compounds have aryl substituents. They are typically prepared by reduction of nitrocompounds, such as the reduction of nitrobenzene with arsenous oxide.[2] Such reactions are proposed to proceed via the intermediacy of the hydroxylamine and nitroso compounds, e.g. phenylhydroxylamine and nitrosobenzene:
- PhNHOH + PhNO → PhN(O)NPh + H2O
Safety
Alkyl azoxy compounds, e.g. azoxymethane are suspected to be genotoxic.[3]
References
- ↑ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "azoxy compounds".
- ↑ H. E. Bigelow and Albert Palmer "Azoybenzene" Org. Synth. 1931, 11, 16. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.011.0016
- ↑ Guideline On The Limits Of Genotoxic Impurities "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-09-04. Retrieved 2007-07-11.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/23/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.