Battle of the Sacramento River
| Battle of the Sacramento River | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Mexican–American War | |||||||
 "Battle of the Sacramento" by F. Bastin | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Alexander Doniphan |
Angel Trias Alvarez Jose A. Heredia | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 940 | 4,120 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
1 killed 8 wounded[1]:156 |
~300 killed ~300 wounded ~40 captured[1]:156 | ||||||
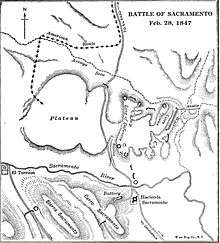
The Battle of the Sacramento River took place on February 28, 1847 during the Mexican–American War. About fifteen miles north of Chihuahua, Mexico at the crossing of the river Sacramento, American forces numbering less than 1,000 men defeated a superior Mexican army which led to the occupation of Chihuahua.[1]:153
Background
On February 8, Colonel Alexander Doniphan's force of 924 soldiers and 300 civilians left El Paso del Norte for Chihuahua despite learning John E. Wool had abandoned his march there.[1]:153 Major Samuel Owens had the civilians formed into a battalion along with the caravan of 312 wagons.[1]:153 On 25 February, the reached the Laguna de Encenillas, where they learned of the Mexican defenses prepared for them.[1]:153
Governor Trias had built up a force under the command of General Jose A. Heredia, consisting of 1200 cavalry (Gen. Garcia Conde: Vera Cruz Dragoons, Durango & Chihuahua Lancers), 1500 infantry (Chihuahua Activos), 119 artillerymen (10 field guns & 6 culverins) and 1000 rancheros.[1]:154 They had constructed a redoubt near the Hacienda Sacramento where the El Paso road crosses the river, and at Hacienda el Torreon two miles to the west.[1]:154
At sunrise on February 28, the last day of February, the Americans took up the line of march and formed the whole wagon train into four columns with the artillery and mounted men in the middle.[1]:154 Three companies screened the front.[1]:154 When the Americans arrived within sight of the Mexican defenses, Doniphan made a reconnaissance of the enemy positions.[1]:154 Twenty-three separate works had been dug for twelve 4- to 9-pounders and nine lighter pieces.[1]:154
Battle
Doniphan used his cavalry to screen the movement of his force parallel to the Arroyo Seco and to the right and out of range of the Mexican artillery.[1]:155 Doniphan formed the wagons into a fort after crossing the gully onto a plateau, and Major Meriwether Lewis Clark, Sr.'s guns fired onto General Garcia Conde's lancers, forcing them to flee.[1]:155
Doniphan's men approached the southernmost Mexican earthworks, held by Heredia's best troops.[1]:155 Doniphan ordered Capt. Richard H. Weightman's twin howitzers to the front accompanied by Capt. Reid's force of mounted cavalry men.[1]:156 Major Owens was killed in the charge, but Missourians took the fort.[1]:155
Trias attempted a counterattack but his lancers were halted by canister shot.[1]:156 By 5 PM the fighting was over.[1]:156
Aftermath
Unable to defend Chihuahua, Trias fled to Parras.[1]:156 Doniphan commented, "The fire of our battery was so effective as to completely silence theirs."[3] Doniphan's men marched into Chihuahua on 2 March and on 23 April was ordered to bring his men to Saltillo, reaching Encantada on 21 May.[1]:157
See also
Gallery
-

Colonel Alexander Doniphan
-

Doniphan's Map from John T. Hughes' 1847 Doniphan's Expedition
References
Additional Reading
- Brooks, N.C. Compete History Of The Mexican War: Grigg, Elliot & Co.Philadelphia 1849, pp.271-280
- Listing of 1846–1848 US Army Casualties
- Cooke, Philip St. George (1964). The Conquest of New Mexico and California, an Historical and Personal Narrative. Albuquerque, NM: Horn and Wallace. p. 89.
External links
- Col. Doniphan's report of the battle
- Marker to Doniphan in Clay Co., MO. - Missouri "Mormon" Frontier Foundation. - John Whitmer Historical Association.
- Doniphan biography. - Kansas "bogus legislature" website.
- Doniphan. - Columbia Encyclopedia.
- Speaking of History Podcast with audio of John Dillingham speech on the life of Alexander Doniphan. - presented at the Truman Presidential Library in May 2007.
- A Continent Divided: The U.S. - Mexico War, Center for Greater Southwestern Studies, the University of Texas at Arlington
Coordinates: 28°52′18″N 106°11′11″W / 28.87167°N 106.18639°W