Bedford Level experiment
The Bedford Level experiment is a series of observations carried out along a six-mile (9.7 km) length of the Old Bedford River on the Bedford Level, Norfolk, England, UK, during the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, to measure the curvature of the Earth. Samuel Birley Rowbotham, who conducted the first few observations, claimed he had proven the Earth to be flat, but after adjusting the method to avoid the effects of atmospheric refraction, Alfred Russel Wallace found a curvature consistent with a spherical Earth.[1]
The Bedford Level
At the point chosen for all the experiments, the river is a slow-flowing drainage canal running in an uninterrupted straight line for a six-mile (9.7 km) stretch to the north-east of the village of Welney. This makes it an ideal location for a direct measurement of the curvature of the Earth, as Rowbotham wrote in Zetectic Astronomy:
- IF the earth is a globe, and is 25,000 English statute miles in circumference, the surface of all standing water must have a certain degree of convexity--every part must be an arc of a circle. From the summit of any such arc there will exist a curvature or declination of 8 inches in the first statute mile. In the second mile the fall will be 32 inches; in the third mile, 72 inches, or 6 feet, as shown in the following diagram:
-
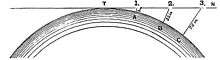 Earth's rate of curvature
Earth's rate of curvature
- ...[A]fter the first few miles the curvature would be so great that no difficulty could exist in detecting either its actual existence or its proportion...In the county of Cambridge there is an artificial river or canal, called the "Old Bedford." It is upwards of twenty miles in length, and []passes in a straight line through that part of the Fens called the "Bedford Level." The water is nearly stationary--often completely so, and throughout its entire length has no interruption from locks or water-gates of any kind; so that it is, in every respect, well adapted for ascertaining whether any or what amount of convexity really exists.[2]
Experiments
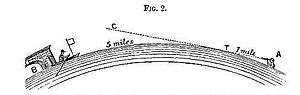
The first experiment at this site was conducted by Rowbotham in the summer of 1838. He waded into the river and used a telescope held eight inches (20 cm) above the water to watch a boat, with a flag on its mast three feet (0.91 m) above the water, row slowly away from him.[3] He reported that the vessel remained constantly in his view for the full six miles (9.7 km) to Welney bridge, whereas, had the water surface been curved with the accepted circumference of a spherical earth, the top of the mast should have been some 11 feet (3.4 m) below his line of sight. He published this observation using the pseudonym Parallax in 1849 and subsequently expanded it into a book, Earth Not a Globe, published in 1865.[4]
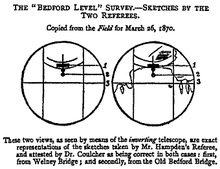
Rowbotham repeated his experiments several times over the years but his claims received little attention until, in 1870, a supporter by the name of John Hampden offered a wager that he could show, by repeating Rowbotham's experiment, that the earth was flat. The noted naturalist and qualified surveyor Alfred Russel Wallace accepted the wager. Wallace, by virtue of his surveyor's training and knowledge of physics, avoided the errors of the preceding experiments and won the bet.[5][6] The crucial step was to set a sight line 13 feet (4 m) above the water, and thereby avoid the effects of atmospheric refraction.[1] Despite Hampden initially refusing to accept the demonstration, Wallace was awarded the bet by the referee, editor of The Field sports magazine. Hampden subsequently published a pamphlet alleging that Wallace had cheated and sued for his money. Several protracted court cases ensued, with the result that Hampden was imprisoned for threatening to kill Wallace[7] and for libel.[8][9] The same court ruled that the wager had been invalid because Hampden retracted the bet and required that Wallace return the money to Hampden. Wallace, who had been unaware of Rowbotham's earlier experiments, was criticized by his peers for "his 'injudicious' involvement in a bet to 'decide' the most fundamental and established of scientific facts".[1]
In 1901, Henry Yule Oldham, a geography reader at King's College, Cambridge, reproduced Wallace's results using three poles fixed at equal height above water level. When viewed through a theodolite (a precision instrument for measuring angles), the middle pole was found to be almost three feet (0.91 m) higher than the poles at each end.[10][11] This version of the experiment was taught in schools until photographs of the Earth from space became available.[12][13]

Advocates of a flat Earth, however, were not defeated: On 11 May 1904 Lady Elizabeth Anne Blount, who would go on to be influential in the formation of the Flat Earth Society, hired a commercial photographer to use a telephoto lens camera to take a picture from Welney of a large white sheet she had placed, touching the surface of the river, at Rowbotham's original position six miles (9.7 km) away. The photographer, Edgar Clifton from Dallmeyer's studio, mounted his camera two feet above the water at Welney and was surprised to be able to obtain a picture of the target, which should have been invisible to him given the low mounting point of the camera. Lady Blount published the pictures far and wide.[14]
These controversies became a regular feature in the English Mechanic magazine in 1904–5, which published Blount's photo and reported two experiments in 1905 that showed the opposite results. One of these, by Clement Stratton on the Ashby Canal, showed a dip on a sight-line only above the surface.[15]
Refraction
Atmospheric refraction can produce the results noted by Rowbotham and Blount. Because the density of air in the Earth's atmosphere decreases with height above the Earth's surface, all light rays travelling nearly horizontally bend downward (assuming a curve or change in air temperature along the line of sight). This phenomenon is routinely allowed for in levelling and celestial navigation.[16]
If the measurement is close enough to the surface, light rays can curve downward at a rate equal to the mean curvature of the Earth's surface. In this case, the two effects of assumed curvature and refraction could cancel each other out and the Earth will appear flat in optical experiments.[17]
This would have been aided, on each occasion, by a temperature inversion in the atmosphere with temperature increasing with altitude above the canal, similar to the phenomenon of the superior image mirage. Temperature inversions like this are common. An increase in air temperature or lapse rate of 0.11 degrees Celsius per metre of altitude would create an illusion of a flat canal, and all optical measurements made near ground level would be consistent with a completely flat surface. If the lapse rate were higher than this (temperature increasing with height at a greater rate), all optical observations would be consistent with a concave surface, a "bowl-shaped earth". Under average conditions, optical measurements are consistent with a spherical Earth approximately 15% less curved than its true diameter.[18] Repetition of the atmospheric conditions required for each of the many observations is not unlikely, and warm days over still water can produce favourable conditions.[19]
Similar experiments conducted elsewhere
On 25 July 1896, Ulysses Grant Morrow, a newspaper editor, conducted a similar experiment on the Old Illinois Drainage Canal, Summit, Illinois. Unlike Rowbotham, he was seeking to demonstrate that the surface of the earth was curved: when he too found that his target marker, 18 inches (46 cm) above water level and five miles (8.0 km) distant, was clearly visible he concluded that the Earth's surface was concavely curved, in line with the expectations of his sponsors, the Koreshan Unity society. The findings were dismissed by critics as the result of atmospheric refraction.[20][21]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Garwood, Christine (2007). Flat Earth. Macmillan. pp. 104–125. ISBN 0-312-38208-1.
- ↑ 'Parallax' (pseud. Samuel Birley Rowbotham) (1881), "Chapter II: Experiments Demonstrating the True Form of Standing Water, and Proving the Earth to be a Plane", Zetetic Astronomy, via sacred-texts.com
- ↑ Rowbotham, Samuel (1863). Zetetic Astronomy. p. 11.
- ↑ Rowbotham, Samuel Birley (writing as "Parallax") (1881). Earth Not a Globe. London: Simpkin, Marshall. ISBN 0-7661-4945-5.
- ↑ "The Rotundity of the Earth". Nature. 1 (23): 581. 7 April 1870. Bibcode:1870Natur...1..581.. doi:10.1038/001581a0.
- ↑ "The Form of the Earth: A Shock of Opinions" (PDF). The New York Times. 10 August 1871. Retrieved 2 November 2007.
- ↑ Wallace, Alfred Russel (1908). My Life. pp. 368–9.
- ↑ Hampden, John (1870). The Bedford Canal Swindle Detected & Exposed. London: A. Bull.
- ↑ Correspondent (8 March 1875). "Spring Assizes". The Times. London. p. 11.
- ↑ Correspondent (25 September 1901). "The British Association". The Times. London (36569): 12.
Mr Yule Oldham on his re-measurement of the curvature of the Earth along the Bedford Level.
- ↑ Oldham, H. Yule (1901). "The experimental demonstration of the curvature of the Earth's surface". Annual Report. London: British Association for the Advancement of Science: 725–6.
- ↑ Association for Science Education (1942). School Science Review. London: John Murray. 24: 120. ISSN 0036-6811. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Richards-Jones, P (1968). "Astronomy at O level". Physics Education. 3 (1): 35–39. Bibcode:1968PhyEd...3...35R. doi:10.1088/0031-9120/3/1/310. ISSN 0031-9120.
- ↑ Michell, John (1984). Eccentric Lives and Peculiar Notions. London: Thames and Hudson. ISBN 0-500-01331-4.
- ↑ Clement Stratton (20 January 1905). English Mechanic. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Umland, Henning. "A short guide to Celestial Navigation". Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- ↑ Umland, pp. 2–5
- ↑ Lynch, David K; Livingston, William (2001). Color and Light in Nature. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-77504-3.
- ↑ Naylor, John (2002). "Mirages". Out of the Blue A 24-Hour Skywatcher's Guide. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-80925-8.
- ↑ Simanek, Donald E. (2003). "Turning the Universe Inside-Out". Lock Haven University of Pennsylvania. Archived from the original on 21 November 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2007.
- ↑ Teed, Cyrus; Morrow, Ulysses Grant (1905). The Earth a Concave Sphere. Estero, FL: Guiding Star. p. 160. ISBN 0-87991-026-7.