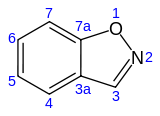
Benzisoxazole
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,2-Benzisoxazole | |||
| Other names
2,1-Benzisoxazole, Anthranil, Benzo[d]isoxazole, Benz[c]isoxazole | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 271-58-9 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:51554 | ||
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL314871 | ||
| ChemSpider | 64227 | ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.437 | ||
| EC Number | 205-980-5 | ||
| PubChem | 67498 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C7H5NO | |||
| Molar mass | 119.12 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 1.18 g/cm3 | ||
| Boiling point | 35 to 38 °C (95 to 100 °F; 308 to 311 K) (at 2.67 hPa) 101-102 °C (at 2 kPa) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| S-phrases | S24/25, S28A, S37, S45 | ||
| Flash point | 58 °C (136 °F; 331 K) | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Benzisoxazole is an aromatic organic compound with a molecular formula C7H5NO containing a benzene-fused isoxazole ring structure.[1][2] Benzisoxazole has no household use. It is used primarily in industry and research.
Being a heterocyclic compound, benzisoxazole finds use in research as a starting material for the synthesis of larger, usually bioactive structures.
It is found within the chemical structures of pharmaceutical drugs such as some antipsychotics (including risperidone, paliperidone, ocaperidone, and iloperidone) and the anticonvulsant zonisamide.
Its aromaticity makes it relatively stable, although as a heterocycle, it has reactive sites which allow for functionalization.
References
- ↑ Katritzky, A. R.; Pozharskii, A. F. (2000). Handbook of Heterocyclic Chemistry (2nd ed.). Academic Press. ISBN 0080429882.
- ↑ Clayden, J.; Greeves, N.; Warren, S.; Wothers, P. (2001). Organic Chemistry. Oxford, Oxfordshire: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-850346-6.
See also
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/27/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.