Beta helix

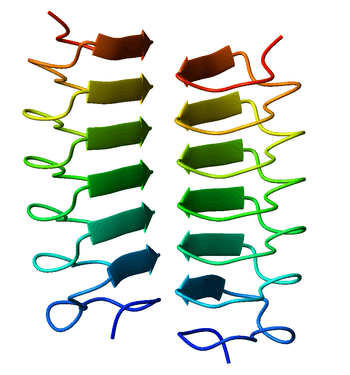
A beta helix is a protein structure formed by the association of parallel beta strands in a helical pattern with either two or three faces. The beta helix is a type of solenoid protein domain. The structure is stabilized by inter-strand hydrogen bonds, protein-protein interactions, and sometimes bound metal ions. Both left- and right-handed beta helices have been identified.
The first beta-helix was observed in the enzyme pectate lyase, which contains a seven-turn helix that reaches 34 Å (3.4 nm) long. The P22 phage tailspike protein, a component of the P22 bacteriophage, has 13 turns and in its assembled homotrimer is 200 Å (20 nm) in length. Its interior is close-packed with no central pore and contains both hydrophobic residues and charged residues neutralized by salt bridges.
Both pectate lyase and P22 tailspike protein contain right-handed helices; left-handed versions have been observed in enzymes such as UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase and archaeal carbonic anhydrase.[1] Other proteins that contain beta helices include the antifreeze proteins from the beetle Tenebrio molitor (right-handed)[2] and from the spruce budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana (left-handed),[3] where regularly spaced threonines on the β-helices bind to the surface of ice crystals and inhibit their growth.
Beta helices can associate with each other effectively, either face-to-face (mating the faces of their triangular prisms) or end-to-end (forming hydrogen bonds). Hence, β-helices can be used as "tags" to induce other proteins to associate, similar to coiled coil segments.
Members of the Pentapeptide repeat family have been shown to possess a quadrilateral beta-helix structure.[4]
References
- ↑ Kisker C, Schindelin H, Alber BE, Ferry JG, Rees DC (May 1996). "A left-hand beta-helix revealed by the crystal structure of a carbonic anhydrase from the archaeon Methanosarcina thermophila". EMBO J. 15 (10): 2323–30. PMC 450161
 . PMID 8665839.
. PMID 8665839. - ↑ Liou YC, Tocilj A, Davies PL, Jia Z (July 2000). "Mimicry of ice structure by surface hydroxyls and water of a beta-helix antifreeze protein". Nature. 406 (6793): 322–4. doi:10.1038/35018604. PMID 10917536.
- ↑ Leinala EK, Davies PL, Jia Z (May 2002). "Crystal structure of beta-helical antifreeze protein points to a general ice binding model". Structure. 10 (5): 619–27. doi:10.1016/s0969-2126(02)00745-1. PMID 12015145.
- ↑ Vetting MW, Hegde SS, Fajardo JE, et al. (January 2006). "Pentapeptide repeat proteins". Biochemistry. 45 (1): 1–10. doi:10.1021/bi052130w. PMC 2566302
 . PMID 16388575.
. PMID 16388575.
- Branden C, Tooze J. (1999). Introduction to Protein Structure 2nd ed. Garland Publishing: New York, NY. pp 84–6.
- Dicker IB and Seetharam S. (1992) "What is known about the structure and function of the Escherichia coli protein FirA?" Mol. Microbiol., 6, 817-823.
- Raetz CRH and Roderick SL. (1995) "A Left-Handed Parallel β Helix in the Structure of UDP-N-Acetylglucosamine Acyltransferase", Science, 270, 997-1000. (Left-handed)
- Steinbacher S, Seckler R, Miller S, Steipe B, Huber R and Reinemer P. (1994) "Crystal structure of P22 tailspike protein: interdigitated subunits in a thermostable trimer", Science, 265, 383-386. (Right-handed)
- Vaara M. (1992) "Eight bacterial proteins, including UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase (LpxA) and three other transferases of Escherichia coli, consist of a six-residue periodicity theme", FEMS Microbiol. Lett, 97, 249-254.
- Yoder MD, Keen NT and Jurnak F. (1993) "New domain motif:the structure of pectate lyase C, a secreted plant virulence factor", Science, 260, 1503-1507. (Right-handed)
External links
- SCOP family of right-handed β-helices
- SCOP family of left-handed β-helices
- CATH β-helix protein family