Caramboxin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
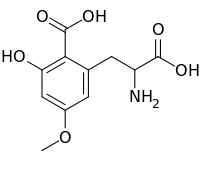
| IUPAC name
2-Carboxy-3-hydroxy-5-methoxyphenylalanine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 32779488 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H13NO6 | |
| Molar mass | 255.23 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Caramboxin (CBX) is a toxin found in star fruit (Averrhoa carambola)).[1] Individuals with some types of kidney disease are susceptible to adverse neurological effects including intoxication, seizures and even death after eating star fruit. Caramboxin has been identified as the neurotoxin responsible for these effects. Caramboxin is a non-proteinogenic amino acid that stimulates the glutamate receptors in neurons. Its chemical structure is similar to the amino acid phenylalanine. Caramboxin is an agonist of both NMDA and AMPA glutamatergic ionotropic receptors with potent excitatory, convulsant, and neurodegenerative properties.[2]
References
- ↑ "Star fruit's chemical curse". C&E News. December 2, 2013: 28.
- ↑ Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Moyses-Neto, M.; Del Vecchio, F.; Oliveira, J. A. C.; Dos Santos, F. L.; Castro, O. W.; Arisi, G. M.; Dantas, M. R.; Carolino, R. O. G.; Coutinho-Netto, J.; Dagostin, A. L. A.; Rodrigues, M. C. A.; Leão, R. M.; Quintiliano, S. A. P.; Silva, L. F.; Gobbo-Neto, L.; Lopes, N. P. (2013). "Elucidating the Neurotoxicity of the Star Fruit". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 52 (49): 13067. doi:10.1002/anie.201305382.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/4/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.