Chach of Alor
| Chach | |
|---|---|
| Maharaja of Sindh | |
| Reign | 631-711 |
| Predecessor | Rai Sahasi (Sinhasena) |
| Successor | Chandar |
| Issue | Dahir |
| House | Brahmin dynasty |
| Religion | Hinduism |
Chach (c. 631-711) (Sindhi: چچ)[1] was a Brahmin who reigned as king of Sindh in the mid-7th century AD. A former prime minister (office) to the king Rai Sahasi II, Chach ascended to the throne[1] by marrying the king's widow. Chach expanded the kingdom of Sindh, and his successful efforts to subjugate surrounding monarchies and ethnic groups into an empire covering the entire Indus valley and beyond were recorded in the Chach Nama.
Biography
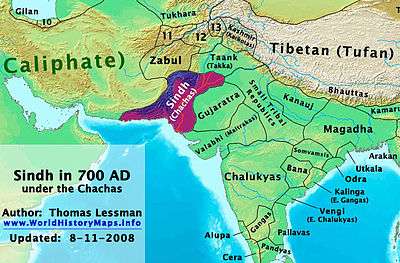
Chach was a Brahmin who rose to a position of influence under Rai Sahiras II, king of Sindh and a member of the Rai dynasty. Chach was given the appointments prime minister[2] to the King, and retained influence after Rai Sahasi's death. He became the lover of Chach's widow, and their marriage enabled him to receive the kingship the date of which is normally put at 632 AD.[1] His claim to the throne was challenged by Rai Sahasi's brother, Rana Maharath, the king of Chittor. Chach defeated and killed Maharath in 640. It is claimed in the Chach Nama that Maharath, seeing that his army was making little headway against that of Chach, devised the sly stratagem of challenging Chach to a duel. Maharath took advantage of the fact that as a trained Kshatriya warrior he would have a decisive advantage over Chach, a Brahmin Court Administrator with very little battle combat training. Chach, knowing he could not refuse the offer of a duel without appearing weak, and understanding clearly the machiavellian brilliance of this offer, realized that he had to use all of his strengths in strategy and diplomacy in order to survive and emerge victorious in this deadly situation. He thought quickly and devised an equally clever stratagem as his response in this high-stakes chess game. Chach claimed that he could not fight on horseback as he was not a trained horseman and suggested that they both fight on foot. Maharath readily agreed knowing that he would have the overwhelming advantage at close quarters. The two dismounted to engage in a duel ensued in which Chach prevailed.
Chach enlisted his brother Chandar (also known as Chandra) to help him administer the kingdom. He then launched a campaign against a succession of autonomous regions; he defeated his opponents along the south bank of the River Beas, at Iskandah, and at Sikkah. He sacked Sikkah, killing 5,000 men and taking the remainder of its inhabitants prisoners. A significant number of these captives were enslaved, and much booty was taken.[2] After this victory, which he appointed a thakur to govern from Multan, and used his army to settle boundary disputes with Kashmir. Chach also conquered Siwistan, but allowed its chief, Matta, to remain as his feudatory.
Later, he expanded his rule into Buddhist regions across the Indus River. These efforts culminated in a battle at Brahmanabad, in which the region's governor, Agham Lohana, was killed. Chach remained in Brahmanabad for a year to cement his authority there, and appointed Agham's son Sarhand as his governor; Sarhand was also wed to Chach's niece. Chach took Agham's widow as his wife, as well.
From Brahmanabad, he invaded Sassanid territory through the town of Armanbelah, marching from Turan to Kandahar. He exacted tribute from the latter before returning.
Upon his death, Chach was succeeded by his brother Chandar; Chandar is stated to have ruled for eight years, whereupon Dahir, Chach's eldest son, inherited the throne.
Islamic expansion
In 644, after the Muslim conquest of Sassanid Empire, the Rashidun army entered Makran and defeated Sindh's army in the Battle of Rasil, annexing Makran (a traditional Persian territory under control of Rai dynasty at that time) and eastern Balochistan. Caliph Umar (634-644), however, for the time being, disapproved of any incursion beyond the Indus river and ordered his subordinates to consolidate their position west of Indus.[3]
Places named after Chach
Several places along the Sindhu River were named after Chach; among these are Chachpur, Chachar, Chachro, Chachgaon, Chachi.[4]
| Preceded by Rai Sahasi II |
Chach of Alor 632-671 AD |
Succeeded by Chandar |
References
- 1 2 3 Wink, André. (1991). Al- Hind, the Making of the Indo-Islamic World: The slave kings and the Islamic conquest. 2, p. 153. Leiden: Brill.
- 1 2 The Chachnamah, An Ancient History of Sind, Giving the Hindu period down to the Arab Conquest. (1900). Translated from the Persian by Mirza Kalichbeg Fredunbeg. Karachi: Commissioners Press.
- ↑ Imperial Gazetteer of India, v. 6, p. 275.
- ↑ Balfour, Edward. (1885). The cyclopaedia of India and of Eastern and Southern Asia, commercial, industrial, and scientific; products of the mineral, vegetable, and animal kingdoms, useful arts and manufactures. London: B. Quaritch, p. 653.