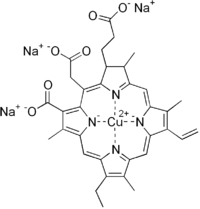
Chlorophyllin
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Natural green 3, E141 | |
| Identifiers | |
| 11006-34-1 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 4586363 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.117 |
| PubChem | 5479494 |
| UNII | 1D276TYV9O |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C34H31CuN4Na3O6 | |
| Molar mass | 724.15 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Chlorophyllin refers to any one of a group of closely related water-soluble salts that are semi-synthetic derivatives of chlorophyll, differing in the identity of the cations associated with the anion. Its most common form is a sodium/copper derivative used as a food additive and in alternative medicine. Chlorophyll is present in green leafy vegetables and reaching levels as high as 5.7% in spinach.[1] As a food coloring agent, copper complex chlorophyllin is known as natural green 3 and has the E number E141.[2]
Uses
Cancer prevention
Because chlorophyll does not dissolve in water, food sources of chlorophyll do not bind to mutagenic substances to a significant extent. Chlorophyllin, being water-soluble, can significantly bind to environmental mutagens such as the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons benzo[a]pyrene[3] and dibenzo{a,i}pyrene.[1] Chlorophyllin binds to mutagens twenty times better than resveratrol and thousands of times better than xanthines.[4]
Medicine and hygiene
Chlorophyllin is the active ingredient in a number of internally taken preparations intended to reduce odors associated with incontinence, colostomies and similar procedures, as well as body odor in general. It is also available as a topical preparation, purportedly useful for both treatment and odor control of wounds, injuries, and other skin conditions—notably radiation burns.
References
- 1 2 Castro DJ, Löhr CV, Fischer KA, Waters KM, Webb-Robertson BJ, Dashwood RH, Bailey GS, Williams DE (2009). "Identifying efficacious approaches to chemoprevention with chlorophyllin, purified chlorophylls and freeze-dried spinach in a mouse model of transplacental carcinogenesi". CARCINOGENESIS. 30 (2): 315–320. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgn280. PMC 2722150
 . PMID 19073876.
. PMID 19073876. - ↑ "Duranat Cu Chlorophyllin WSP (Natural Green 3-1 CI 75810-1)". Retrieved 15 October 2012.
- ↑ Keshava C, Divi RL, Einem TL, Richardson DL, Leonard SL, Keshava N, Poirier MC, Weston A (2009). "Chlorophyllin significantly reduces benzo[a]pyrene-DNA adduct formation and alters cytochrome P450 1A1 and 1B1 expression and EROD activity in normal human mammary epithelial cells". ENVIRONMENTAL AND MOLECULAR MUTAGENESIS. 50 (2): 134–144. doi:10.1002/em.20449. PMC 2637934
 . PMID 19152381.
. PMID 19152381. - ↑ Osowski A, Pietrzak M, Wieczorek Z, Wieczorek J (2010). "Natural compounds in the human diet and their ability to bind mutagens prevents DNA-mutagen intercalation". JOURNAL OF TOXICOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH, PART A. 73 (17-18): 1141–1149. doi:10.1080/15287394.2010.491044. PMID 20706936.
External links
- Chlorophyll and Chlorophyllin, Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University
- 2002 Video from CNN
- Food-Info.net