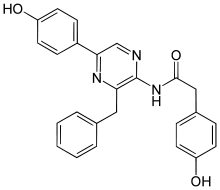
Coelenteramide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-[2-benzyl-6-(4-oxocyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-ylidene)-1H-pyrazin-3-yl]-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide | |
| Other names
Coelenteramide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 50611-86-4 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | [1].html 4484099[2] |
| PubChem | 5326781 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H21N3O3 | |
| Molar mass | 411.45254 |
| Density | 1.26 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 678.298 °C (1,252.936 °F; 951.448 K) at 760 mmHg |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 364.022 °C (687.240 °F; 637.172 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Coelenteramide is the oxidized product, or oxyluciferin, of the bioluminescent reactions in many marine organisms that use coelenterazine. It was first isolated as a blue fluorescent protein from Aequorea victoria after the animals were stimulated to emit light.[3] Under basic conditions, the compound will break down further into coelenteramine and 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid.
It is an aminopyrazine.[4]
References
- ↑ http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.4484099.html (accessed 22:19, Jun 6, 2012)
- ↑ http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.4484099.html (accessed 22:19, Jun 6, 2012)
- ↑ Shimomura O, Johnson FH (1975). "Chemical Nature of Bioluminescence Systems in Coelenterates". PNAS USA. 72 (4): 1546–1549. doi:10.1073/pnas.72.4.1546. PMC 432574
 . PMID 236561.
. PMID 236561. - ↑ Discovery and Validation of a New Family of Antioxidants: The Aminopyrazine Derivatives. M. L. N. Dubuisson, J.-F. Rees and J. Marchand-Brynaert, Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry, 2004, 4, 159-165, doi:10.2174/1389557043403927
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 1/28/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.