Cryogenine
This article is about the alkaloid from the plants in the genus Heimia. For the antipyretic drug, see Phenicarbazide.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | none |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
10308-13-1 |
| PubChem (CID) | 5315204 |
| ChemSpider |
4474587 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1173218 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H29NO5 |
| Molar mass | 435.512 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
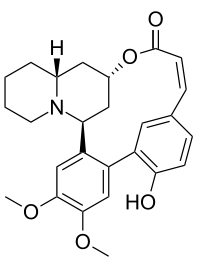
Cryogenine, also known as vertine or (10α)-4,5-dimethoxy-2-hydroxylythran-12-one, is a biphenylquinolizidine lactone alkaloid from the plants Sinicuichi (Heimia salicifolia) and H. myrtifolia. The compound has no psychoactive properties in humans up to 310 mg, but has shown anti-inflammatory activity similar to aspirin.[1]
The freebase form melts at 250–251 °C and is soluble in moderately polar organic solvents such as chloroform, methylene chloride, benzene, and methanol, but is insoluble in water and petroleum ether.
In the development of thin layer chromatography plates with diazotized p-nitroaniline spray, cryogenine produces a purple spot (as does sinicuichine, another biphenylquinolizidine lactone alkaloid found in Heimia species).
See also
References
- ↑ M. H. Malone, A. Rother (1994). "Heimia salicifolia: A phytochemical and phytopharmacologic review". J. Ethnopharmacol. 42 (3): 135–159. doi:10.1016/0378-8741(94)90080-9. PMID 7934084.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 12/30/2013. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.