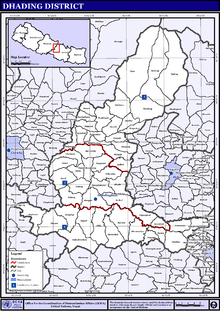
Dhading District
| Dhading धादिङ जिल्ला | |
|---|---|
| District | |
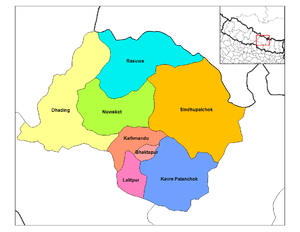 Location of Dhading | |
| Country | Nepal |
| Region | Central (Madhyamanchal) |
| Zone | Bagmati |
| Headquarters | Dhading Besi |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,926 km2 (744 sq mi) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 336,067[1] |
| Time zone | NPT (UTC+5:45) |
| Website |
www |
Dhading District (Nepali: धादिङ जिल्ला![]() Listen , a part of Province No. 3, is one of the seventy-five districts of Nepal. The district, with Dhading Besi as its district headquarters, covers an area of 1,926 square kilometres (744 sq mi), had a population of 338,658 in 2001[2] and 336,067 in 2011.[1]
Listen , a part of Province No. 3, is one of the seventy-five districts of Nepal. The district, with Dhading Besi as its district headquarters, covers an area of 1,926 square kilometres (744 sq mi), had a population of 338,658 in 2001[2] and 336,067 in 2011.[1]
Geography and climate
The district spreads from 27'40" E to 28'17" E and 80'17"N to 84'35"N.[3] The mountain range Ganesh Himal is the predominate mountain range located within Dhading. Some of the peaks are over 7,000 metres (23,000 ft). The 8,000-metre (26,000 ft) plus mountain Manaslu is clearly visible from much of Dhading, although it is located within the bounds of Gorkha. The transnational Prithivi Highway connecting Kathmandu and Pokhara runs through the southern portion of the district making for easy access to the Kathmandu valley. The road parallels the Trishuli River. The western border with Gorkha is bisected by the Budhigandaki River.
The district is bounded by
Dhading is the only district of Nepal which ranges from the mountain Ganesh Himal to the Churevawar pradesh of Terai (Chitwan). The district, with Dhading Besi as its district headquarters, covers an area of 1,926 square kilometres (744 sq mi) and has a population (2001) of 338,658.[2] The mountain range "Ganesh" is the predominated mountain range located within Dhading. All of the peaks are over 7,000 metres (23,000 ft) with some approaching 8,000 metres (26,000 ft). The 8,000-metre (26,000 ft) plus mountain "Manaslu" is clearly visible from much of Dhading, although it is located within the bounds of Gorkha. The transnational "King Prithivi Highway" connecting Kathmandu and Pokhara runs through the southern portion of the district making for easy access too the Kathmandu valley. The road parallels the Trishuli River. Dhading is 80% farmland and 20% forest. The western border with Gorkha is bisected by the Budhigandaki River, one of the prettiest rivers of Nepal.
| Climate Zone[4] | Elevation Range | % of Area |
|---|---|---|
| Upper Tropical | 300 to 1,000 meters 1,000 to 3,300 ft. |
39.7% |
| Subtropical | 1,000 to 2,000 meters 3,300 to 6,600 ft. |
35.1% |
| Temperate | 2,000 to 3,000 meters 6,400 to 9,800 ft. |
10.8% |
| Subalpine | 3,000 to 4,000 meters 9,800 to 13,100 ft. |
7.7% |
| Alpine | 4,000 to 5,000 meters 13,100 to 16,400 ft. |
3.2% |
| Nival | above 5,000 meters | 2.5% |
The people of the district are primarily Bhramin and Chetri in the south and Tamang and Gurung in the north, with much of the center Newari. Gurkha route, the birthplace of founder of Nepal King Prithivi Naryan Shah crosses through Dhading.
Rivers
The main river of the district is Ankhu Khola which comes from Ganesh Himal and passes through Khahare Tripureshwor and Salyantar and meets Budhi Gandaki at Narsingha Dhamm . Budhi Gandaki separates the district from Gorkha district. There are 25 small rivers, the main being Charoudi, Malekhu, Galtukhola, Belkhukhola, Chirandikhola, Maheshkhola, Thopal, Manukhola, Kastekhola, Mastekhola. Besides these, there are over 1743 smaller rivers, springs and seasonal streams.[5]
Demography
The people of the district are primarily Brahmin and Chhetri in the south and Ghale, Gurung and Tamang in the north, with much of the center Newari. The famous King Prithivi Naryan Shah/Gurkha route crosses through Dhading.
Religious temple
Dhading District has many religious temples. Among them Tripurasundari Mai is one of the famous in Nepal as well, which lies in the northern part of the district. Similarly Siddha than in Salang VDC is a famous Hindu religious site. Others are Bhairabi Temple in Sunaula Bazar.
Tourism
Dhading has huge potential of tourism and is getting popularity in the tourism industry.[6]
Towns and villages
See also
References
- 1 2 "National Population and Housing Census 2011(National Report)" (PDF). Central Bureau of Statistics. Government of Nepal. November 2012. Retrieved November 2012. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - 1 2 "Nepal Census 2001". Nepal's Village Development Committees. Digital Himalaya. Retrieved 12 December 2008.
- ↑ "District Development Committee, Dhading".
- ↑ The Map of Potential Vegetation of Nepal - a forestry/agroecological/biodiversity classification system (PDF), . Forest & Landscape Development and Environment Series 2-2005 and CFC-TIS Document Series No.110., 2005, ISBN 87-7903-210-9, retrieved Nov 22, 2013 horizontal tab character in
|series=at position 91 (help) - ↑ Book:Jilla Bastugat Biwaran:Dhading-2064, Page 3, Language: Nepali, Nepal Government Publication
- ↑ "Dhading Village Tours Nepal - 10 Days".
External links
Coordinates: 27°52′0″N 84°55′0″E / 27.86667°N 84.91667°E
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dhading District. |
