Dihydrokavain
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
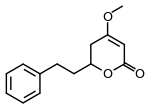
| IUPAC name
4-methoxy-2-phenethyl-2,3-dihydropyran-6-one | |
| Other names
Dihydrokawain Marindinin | |
| Identifiers | |
| 587-63-3 19451-52-6 19902-90-0 24576-85-0 3384-26-7 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 88817 |
| PubChem | 98356 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H16O3 | |
| Molar mass | 232.27 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Dihydrokavain is one of the six major kavalactones found in the kava plant.[1] It appears to contribute significantly to the anxiolytic effects of kava, based on a study in chicks.[2]
References
- ↑ Malani, Joji (2002-12-03). "Evaluation of the effects of Kava on the Liver" (PDF). Fiji School of Medicine. Retrieved 2009-09-04.
- ↑ Feltenstein, MW; LC Lambdin; M Ganzera; H Ranjith; W Dharmaratne; NP Nanayakkara; IA Khan; KJ Sufka (March 2003). "Anxiolytic properties of Piper methysticum extract samples and fractions in the chick social-separation-stress procedure.". Phytotherapy Research: PTR. 17 (3): 210–216. doi:10.1002/ptr.1107. PMID 12672148.
| History | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical composition |
| ||||||||||
| Alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids | |
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents |
|
| Monoureides |
|
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines |
|
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
See also: GABAergics | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/10/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.