Diphenylketene
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,2-Di(phenyl)ethenone | |
| Other names
Diphenylethenone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 525-06-4 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 109691 |
| PubChem | 123069 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H10O | |
| Molar mass | 194.23 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Red-orange oil |
| Melting point | 8 to 9 °C (46 to 48 °F; 281 to 282 K) |
| Boiling point | 118 to 120 at 1mmHg |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Diphenylketene is a chemical substance of the ketene family. Diphenylketene, like most disubstituted ketenes, is a red-orange oil at room temperature and pressure.
Reactivity
Diphenylketene can undergo attack from a host of nucleophiles, including alcohols, amines, and enolates with fairly slow rates. These rates can be increased in the presence of catalysts. At present the mechanism of attack is unknown, but work is underway to determine the exact mechanism.
Synthesis
Diphenylketene is produced by the elimination of hydrogen chloride from diphenylacetyl chloride in the presence of triethylamine.[1]
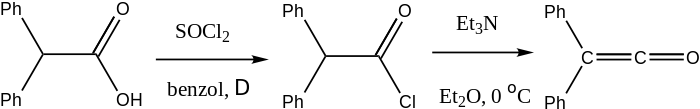
Preparation of Diphenylketene
References
- ↑ Submitted by Edward C. Taylor Alexander McKillop, and George H. Hawks. Checked by C. J. Michejda, D. D. von Riesen, R. W. Comnick, and Henry E. Baumgarten. (1972). "DIPHENYLKETENE [Ethenone, diphenyl-]". Organic Syntheses. 52: 36. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.052.0036.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/7/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.