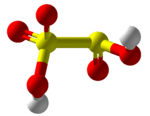
Disulfurous acid
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
disulfurous acid [1] | |||
| Other names
pyrosulfurous acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:29252 | ||
| ChemSpider | 26062 | ||
| PubChem | 28020 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| H2S2O5 | |||
| Molar mass | 146.14 g mol−1 | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Disulfurous acid or pyrosulfurous acid is an oxoacid of sulfur with the formula H2S2O5. The salts of disulfurous acid are called disulfites or metabisulfites. Disulfurous acid is, like sulfurous acid (H2SO3), a phantom acid, which does not exist in the free state. [2] In contrast to disulfate (S2O7−), disulfite has two directly connected sulfur atoms. The oxidation state of the sulfur atom bonded to 3 oxygen atoms is +5 while oxidation number of other sulfur atom is +3.
References
- ↑ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2005). Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry (IUPAC Recommendations 2005). Cambridge (UK): RSC–IUPAC. ISBN 0-85404-438-8. p. 130. Electronic version.
- ↑ Holleman, Wiberg: Inorganic chemistry Academic Press @ Google Books. 2001; pp. 537-540.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/21/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.