Dithiazanine iodide
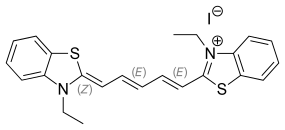 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-Ethyl-2-[5-(3-ethyl-2-benzothiazolinylidene)-1,3-pentadienyl]-benzothiazolium iodide | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
3-Ethyl-2-[(1E,3E,5Z)-5-(3-ethyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)penta-1,3-dien-1-yl]-1,3-benzothiazol-3-ium iodide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 514-73-8[1] | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL421701 |
| ChemSpider | 4642986 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.443 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H23IN2S2 | |
| Molar mass | 518.48 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Green crystals |
| Melting point | Decomposes at 478.4 °F (248.0 °C) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dithiazanine iodide is a chemical compound.[1] It is used as a veterinary anthelmintic for dogs.[3] It is a highly toxic chemical, with a lethal dose for humans of about 4–16 mg/kg by oral ingestion. The mechanism of toxicity is not well known but it is believed that this chemical interferes with cells' absorption of glucose, which is essential to obtain energy through cell respiration.
See also
- Alazanine triclofenate
References
- 1 2 Cameo Chemicals. "Chemical data". NOAA. Retrieved September 19, 2011.
- 1 2 "Chemspider data". Chemspider. Retrieved September 19, 2011.
- ↑ "Law about use". Justia. Retrieved September 19, 2011.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/27/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.