Edifenphos
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
O-Ethyl-S,S-diphenyldithiophosphate; EDDP | |
| Identifiers | |
| 17109-49-8 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:34735 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1671900 |
| ChemSpider | 26320 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.037.420 |
| KEGG | C14436 |
| PubChem | 28292 |
| UNII | 770M9U0F8Q |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
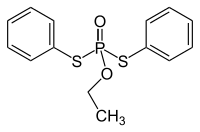
| C14H15O2PS2 | |
| Molar mass | 310.37 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.23 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | −25 °C (−13 °F; 248 K)[1] |
| 56 mg/L (20 °C)[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   [1] [1] |
| GHS signal word | Danger |
| H301, H311, H331, H317, H410[1] | |
| P261, P273, P280, P301+310, P311, P501[1] | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Edifenphos (O-ethyl-S,S-diphenyldithiophosphate, EDDP) is a systemic fungicide that inhibits phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis.[2][3] It was introduced in 1966 by Bayer to combat blast fungus and Pellicularia sasakii in rice cultivation.[3] It was never authorized for use in the EU.[4]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Record of Edifenphos in the GESTIS Substance Database of the IFA, accessed on 2016-02-01
- ↑ Kodama, Osamu; Yamashita, Kenji; Akatsuka, Tadami (1980). "Edifenphos, Inhibitor of Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis in Pyricularia oryzae". Agricultural and Biological Chemistry. 44 (5): 1015–1021. doi:10.1080/00021369.1980.10864095.
- 1 2 Matolcsy, György; Nádasy, Miklós; Andriska, Viktor; Terényi, Sándor (1989). Pesticide Chemistry. Elsevier. p. 306. ISBN 978-0444989031.
- ↑ "Edifenphos: Not Approved". EU Pesticides Database Active Substances. Retrieved 2016-02-01.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/25/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.