Epicocconone
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
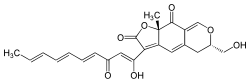
| IUPAC name
(6S,9aS)-6-(Hydroxymethyl)-3-[(1Z,4E,6E,8E)-1-hydroxy-3-oxodeca-1,4,6,8-tetraen-1-yl]-9a-methyl-5,6-dihydro-2H-furo[3,2-g]isochromene-2,9(9aH)-dione | |
| Other names
Deep Purple Lava Purple | |
| Identifiers | |
| 371163-96-1 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:51226 |
| ChemSpider | 8398759 |
| PubChem | 56464320 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H22O7 | |
| Molar mass | 410.42 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Epicocconone is long Stokes' shift fluorescent dye found in the fungus Epicoccum nigrum.[1] Though weakly fluorescent in water (green emission, 520 nm) it reacts reversibly with proteins to yield a product with a strong orange-red emission (610 nm).[2] This dye can be used as a sensitive total protein stain for 1D and 2D electrophoresis,[3] quantitative determination of protein concentration,[4] making it a powerful loading control for Western blots.[5]
Synthetic variant
In addition to the natural variant from the fungus, there are several synthetic analogs.[6] With respect to protein staining properties there are few differences between natural and synthetic analogs.
Commercial sources
Epicocconone is available from Fluorotechnics Australia. It is also the active ingredient in Deep Purple Total Protein Stain (GE Healthcare), FluoroProfile (Sigma-Aldrich) and LavaCell (Fluorotechnics).
References
- ↑ Bell, P. J. L.; Karuso, P. (2003). "Epicocconone, A Novel Fluorescent Compound from the FungusEpicoccumnigrum". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 125 (31): 9304–9305. doi:10.1021/ja035496+. PMID 12889954.
- ↑ Choi, H. -Y.; Veal, D. A.; Karuso, P. (2005). "Epicocconone, A New Cell-Permeable Long Stokes' Shift Fluorescent Stain for Live Cell Imaging and Multiplexing". Journal of Fluorescence. 16 (4): 475–482. doi:10.1007/s10895-005-0010-7. PMID 16328703.
- ↑ MacKintosh, J. A.; Choi, H. Y.; Bae, S. H.; Veal, D. A.; Bell, P. J.; Ferrari, B. C.; Van Dyk, D. D.; Verrills, N. M.; Paik, Y. K.; Karuso, P (2003). "A fluorescent natural product for ultra sensitive detection of proteins in one-dimensional and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis". Proteomics. 3 (12): 2273–88. doi:10.1002/pmic.200300578. PMID 14673778.
- ↑ MacKintosh, J. A.; Veal, D. A.; Karuso, P. (2005). "Fluoroprofile, a fluorescence-based assay for rapid and sensitive quantitation of proteins in solution". Proteomics. 5 (18): 4673–4677. doi:10.1002/pmic.200500095. PMID 16267819.
- ↑ Moritz, C. P.; Marz, S. X.; Reiss, R; Schulenborg, T; Friauf, E (2014). "Epicocconone staining: A powerful loading control for Western blots". Proteomics. 14 (2–3): 162–8. doi:10.1002/pmic.201300089. PMID 24339236.
- ↑ Peixoto, P. A.; Boulangé, A; Ball, M; Naudin, B; Alle, T; Cosette, P; Karuso, P; Franck, X (2014). "Design and synthesis of epicocconone analogues with improved fluorescence properties". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 136 (43): 15248–56. doi:10.1021/ja506914p. PMID 25271695.