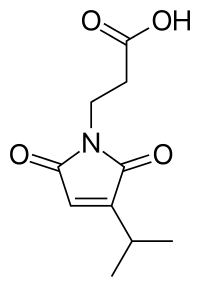
Farinomalein
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-(2,5-dioxo-3-propan-2-ylpyrrol-1-yl)propanoic acid | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
3-(3-isopropyl-2,5-dioxo-pyrrol-1-yl)propanoic acid | |
| Other names
2,5-dihydro-3-(1-methylethyl)-2,5-dioxo-1H-pyrrole-1-propanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 1175521-35-3 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:718704 |
| ChemSpider | 24674945 |
| PubChem | 44254797 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H13NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 211.21 g/mol |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Density | 1.281 (ACD/Labs) |
| Melting point | 75 to 77 °C (167 to 171 °F; 348 to 350 K) |
| Boiling point | 384.6 °C (724.3 °F; 657.8 K) Calculated (ACD/Labs) |
| Solubility | CH2Cl2, acetone, toluene, CH3OH |
| log P | 1.34 (ACD/Labs) |
| Vapor pressure | 0 mmHg (25 °C) |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases | R43 |
| S-phrases | S22, S24, S37, S61. |
| Flash point | 86.4 °C (187.5 °F; 359.5 K) (ACD/Labs) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Farinomalein is a natural maleimide with formula C10H13NO4 - was first isolated from the entomopathogenic fungus Isaria farinosa (Paecilomyces farinosus) - source H599 (Japan).[1]
Farinomalein has shown potent and selective inhibition (0.15-5 μg/disk) against eight isolates of plant pathogenic Phytophthora sojae.[2] These results suggest that farinomalein might be useful as a candidate pesticide for the treatment of Phytophthora stem rot in soybean.[2]
Synthesis
A simple two-stage synthesis from the γ-hydroxybutenolide compound, 5-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-5(H)-furanone, has been reported.[3] Firstly, 5-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-5(H)-furanone is oxidised to 3-isopropylfuran-2,5-dione by Dess–Martin periodinane, followed by acetic acid reflux with beta-alanine. The white powdered product has a melting point of 75-77 °C.
References
- ↑ Sastia P. Putri, Hiroshi Kinoshita, Fumio Ihara, Yasuhiro Igarashi and Takuya Nihira. Farinomalein, a Maleimide-Bearing Compound from the Entomopathogenic Fungus Paecilomyces farinosus. J. Nat. Prod., 2009, 72 (8), pp 1544-1546 doi:10.1021/np9002806
- 1 2 Sastia Prama Putri, Hiroshi Kinoshita, Masayasu Kato and Takuya Nihira. Antimicrobial and antioomycete activities of the novel antibiotic farinomalein. Poster Presentation 2P-2124, Annual Conference, The Society for Bioscience and Bioengineering, Japan, 28 October 2010.
- ↑ William H. Miles and Ming Yan. Synthesis of farinomalein. Tetrahedron Letters, 2010, 51 (13), pp 1710-1712 doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2010.01.083