Foville's syndrome
| Foville's syndrome | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Pons | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | neurology |
| ICD-10 | G46.3 |
| ICD-9-CM | 344.89 |
| DiseasesDB | 32782 |
| MeSH | D020526 |
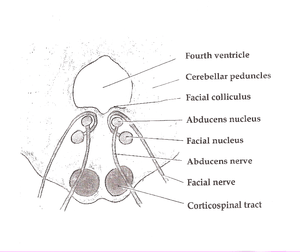
Foville's syndrome is caused by the blockage of the perforating branches of the basilar artery in the region of the brainstem known as the pons.[1]
Structures affected by the infarct are the PPRF, nuclei of cranial nerves VI and VII, corticospinal tract, medial lemniscus, and the medial longitudinal fasciculus.
Presentation
This produces ipsilateral horizontal gaze palsy and facial nerve palsy and contralateral hemiparesis, hemisensory loss, and internuclear ophthalmoplegia.
History
Foville's syndrome was initially described by Achille-Louis-François Foville, a French physician, in 1859.[2]
References
- ↑ 1134166052 at GPnotebook
- ↑ Foville, ALF (1859). "Note sur une paralysie peu connue de certains muscles de l'oeil, et sa liaison avec quelques points de l'anatomie de la physiologie de la protubérance annulaire". Gazette hebdomadaire de médecine et de chirurgie. 6: 146.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 3/23/2014. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.