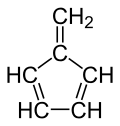
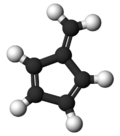
Fulvene
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
5-Methylidenecyclopenta-1,3-diene[1] | |||
| Other names | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 497-20-1 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:51999 | ||
| ChemSpider | 120097 | ||
| PubChem | 136323 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H6 | |||
| Molar mass | 78.11 g·mol−1 | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Fulvene is one of several hydrocarbons with the same formula as benzene, C6H6. The fulvenes are the class of molecules based on this simple hydrocarbon skeleton;[2] the parent chemical, fulvene itself, is rarely encountered.[3] Thiele is credited with discovering the scope of the reaction between cyclopentadiene and aldehydes and ketones that yields the brightly coloured fulvene derivatives.[4] Most fulvenes are still prepared by this route, starting from cyclopentadiene or its sodium cyclopentadienyl anionic form.[5] Modern synthesis of fulvenes now employ protic solvents and catalytic amounts of amines which result in much higher yields.[6]
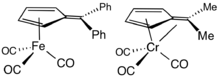
Ligand in organometallic chemistry
2,3,4,5-Tetramethylfulvene, abbreviated Me4Fv, is a relatively common ligand in organometallic chemistry. It typically results from the deprotonation of cationic pentamethylcyclopentadienyl complexes.[7] Some Me4Fv complexes are called tuck-in complexes.
See also
References
- 1 2 Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 379. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "Fulvenes".
- ↑ Bergmann, E. D. (1968). "Fulvenes and Substituted Fulvenes". Chemical Reviews. 68: 41–84. doi:10.1021/cr60251a002.
- ↑ Thiele, J. (1900). "Ueber Ketonreactionen bei dem Cyclopentadiën". Chemische Berichte. 33: 666–673. doi:10.1002/cber.190003301113.
- ↑ Hafner, K.; Vöpel, K. H.; Ploss, G.; König, C. (1973). "6-(Dimethylamino)fulvene" (PDF). Organic Syntheses Coll. Vol. 5: 431.
- ↑ Coşkun, Necdet; Erden, Ihsan (2011-11-11). "An efficient catalytic method for fulvene synthesis". Tetrahedron. 67 (45): 8607–8614. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2011.09.036. ISSN 0040-4020. PMC 3196336
 . PMID 22021940.
. PMID 22021940. - ↑ Kreindlin, A. Z.; Rybinskaya, M. A. (2004). "Cationic and Neutral Transition Metal Complexes with a Tetramethylfulvene or Trimethylallyldiene Ligand". Russian Chemical Reviews. 73 (5): 417–432. doi:10.1070/RC2004v073n05ABEH000842.