GQM-163 Coyote
| GQM-163 Coyote | |
|---|---|
 A GQM-163A Coyote test launch in May 2004. | |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Orbital Sciences |
| Specifications | |
| Length | 5.62m (18 ft 5.2 in) (without booster), 9.56m (31 ft 4.2 in) (incl. booster) |
| Diameter | 35 cm (13.8 in), booster: 46 cm (17.99 in) |
|
| |
| Propellant | Aerojet MARC-R-282 solid-fueled ducted rocket/ramjet engine |
Operational range | 45 nmi (84 km) [1] |
| Flight ceiling | 55,000 feet |
| Flight altitude | Sea-skimming: 30 feet (cruise phase), 15ft (terminal phase) |
| Boost time | Hercules MK 70 solid-fueled rocket |
| Speed | Mach 3.0-4.0 at 5,000-55,000ft, Mach 2.6 at 30-15ft [2] |

A GQM-163A Coyote flies over the bow of a U.S. Navy observation ship during a routine test.
The GQM-163 Coyote is a supersonic sea skimming target built by Orbital Sciences and used by the United States Navy as a successor to the MQM-8 Vandal. Orbital's proposal was chosen over the MA-31, a joint venture between Boeing and Zvezda-Strela. Orbital was awarded their contract for the development of the Coyote SSST in June 2000.
The Coyote is initially boosted by a Hercules MK-70 booster, of similar design to those used by the now obsolete RIM-67 Standard ER missiles. After the booster stage is expended the missile switches to an Aerojet MARC-R-282 solid-fuel rocket /ramjet engine for sustaining its flight. [3][4][5]
Operators
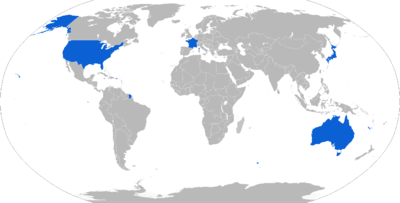
Map with CQM-163 operators in blue
Current operators
References
- ↑
- ↑
- ↑ Aster Slays The Russian Dragon
- ↑ Directory of US Military Rockets and Missiles
- ↑ "GQM-163 SSST: A Tricky Coyote to Match Wits With Defenses". Retrieved 2010-08-17.
- ↑ ANZAC upgrade completes final acceptance trial
- ↑ Latest GQM-163 SSST contract includes first sale to Japan
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/18/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.