Gaussian network model
The Gaussian network model (GNM) is a representation of a biological macromolecule as an elastic mass-and-spring network to study, understand, and characterize mechanical aspects of its long-scale dynamics. The model has a wide range of applications from small proteins such as enzymes composed of a single domain, to large macromolecular assemblies such as a ribosome or a viral capsid. Protein domain dynamics plays key roles in a multitude of molecular recognition and cell signalling processes. Protein domains, connected by intrinsically disordered flexible linker domains, induce long-range allostery via protein domain dynamics. The resultant dynamic modes cannot be generally predicted from static structures of either the entire protein or individual domains.
The Gaussian network model is a minimalist, coarse-grained approach to study biological molecules. In the model, proteins are represented by nodes corresponding to alpha carbons of the amino acid residues. Similarly, DNA and RNA structures are represented with one to three nodes for each nucleotide. The model uses the harmonic approximation to model interactions, i.e. the spatial interactions between nodes (amino acids or nucleotides) are modeled with a uniform harmonic spring. This coarse-grained representation makes the calculations computationally inexpensive.
At molecular level, many biological phenomena, such as catalytic activity of an enzyme, occur within the range of nano- to millisecond timescales. All atom simulation techniques, such as molecular dynamics, rarely reach microsecond trajectory length, depending on the size of the system and accessible computational resources. Normal mode analysis in the context of GNM or elastic network (EN) models, in general, provides insights on the longer-scale functional behaviors of macromolecules. Here, the model captures native state functional motions of a biomolecule in the cost of atomic detail. The inference obtained from this model is complementary to atomic detail simulation techniques.
Another model for protein dynamics based on elastic mass-and-spring networks is the Anisotropic Network Model.
Gaussian network model theory

The Gaussian network model was first proposed in 1996 by Tirion at the atomic level[1] and then one year later reconsidered at the amino-acid level by Bahar, Atilgan, Haliloglu and Erman.[2][3] The model was influenced by work of PJ Flory on polymer networks [4] and other works that utilized normal mode analysis and simplified harmonic potentials to study dynamics of proteins.[5]
The elastic network
Figure 2 shows a schematic view of elastic network studied in GNM. Metal beads represent the nodes in this Gaussian network (residues of a protein) and springs represent the connections between the nodes of this network (covalent and non-covalent interactions between residues). For nodes i and j, equilibrium position vectors, R0i and R0j, equilibrium distance vector, R0ij, instantaneous fluctuation vectors, ΔRi and ΔRj, and instantaneous distance vector, Rij, are shown in Figure 2. Instantaneous position vectors of these nodes are defined by Ri and Rj. The difference between equilibrium position vector and instantaneous position vector of residue i gives the instantaneous fluctuation vector, ΔRi = Ri - R0i. Hence, the instantaneous fluctuation vector between nodes i and j is expressed as ΔRij = ΔRj - ΔRi = Rij - R0ij.
Potential of the Gaussian network
Using the harmonic potential approximation, potential energy of the network in terms of ΔRi is
where γ is a force constant uniform for all springs and Γij is the ijth element of the Kirchhoff (or connectivity) matrix of inter-residue contacts, Γ, defined by
rc is a cutoff distance for spatial interactions and taken to be 7 Å for proteins.
Expressing the X, Y and Z components of the fluctuation vectors ΔRi as ΔXT = [ΔX1 ΔX2 ..... ΔXN], ΔYT = [ΔY1 ΔY2 ..... ΔYN], and ΔZT = [ΔZ1 ΔZ2 ..... ΔZN], above equation simplifies to
Statistical mechanics foundations
In the GNM, the probability distribution of all fluctuations, P(ΔR) is isotropic
and Gaussian
where kB is the Boltzmann constant and T is the absolute temperature. p(ΔY) and p(ΔZ) are expressed similarly. N-dimensional Gaussian probability density function with random variable vector x, mean vector μ and covariance matrix Σ is
normalizes the distribution and |Σ| is the determinant of the covariance matrix.
Similar to Gaussian distribution, normalized distribution for ΔXT = [ΔX1 ΔX2 ..... ΔXN] around the equilibrium positions can be expressed as
The normalization constant, also the partition function ZX, is given by
where is the covariance matrix in this case. ZY and ZZ are expressed similarly. This formulation requires inversion of the Kirchhoff matrix. In the GNM, the determinant of the Kirchhoff matrix is zero, hence calculation of its inverse requires eigenvalue decomposition. Γ−1 is constructed using the N-1 non-zero eigenvalues and associated eigenvectors. Expressions for p(ΔY) and p(ΔZ) are similar to that of p(ΔX). The probability distribution of all fluctuations in GNM becomes
For this mass and spring system, the normalization constant in the preceding expression is the overall GNM partition function, ZGNM,
Expectation values of fluctuations and correlations
Based on the statistical mechanics foundations of GNM, expectation values of residue fluctuations, <ΔRi2>, and correlations, <ΔRi · ΔRj>, can be calculated. Covariance matrix for ΔX is given by
Since,
<ΔRi2> and <ΔRi · ΔRj> follows
Mode decomposition
The GNM normal modes are found by diagonalization of the Kirchhoff matrix, Γ = UΛUT. Here, U is a unitary matrix, UT = U−1, of the eigenvectors ui of Γ and Λ is the diagonal matrix of eigenvalues λi. The frequency and shape of a mode is represented by its eigenvalue and eigenvector, respectively. Since the Kirchhoff matrix is positive semi-definite, the first eigenvalue, λ1, is zero and the corresponding eigenvector have all its elements equal to 1/√N. This shows that the network model is translation invariant.
Cross-correlations between residue fluctuations can be written as a sum over the N-1 nonzero modes as
It follows that, [ΔRi · ΔRj], the contribution of an individual mode is expressed as
where [uk]i is the ith element of uk.
Influence of local packing density
By definition, a diagonal element of the Kirchhoff matrix, Γii, is equal to the degree of a node in GNM that represents the corresponding residue’s coordination number. This number is a measure of the local packing density around a given residue. The influence of local packing density can be assessed by series expansion of Γ−1 matrix. Γ can be written as a sum of two matrices, Γ = D + O, containing diagonal elements and off-diagonal elements of Γ.
- Γ−1 = (D + O)−1 = [ D (I + D−1O) ]−1 = (I + D−1O)−1D−1 = (I - D−1O + ...)−1D−1 = D−1 - D−1O D−1 + ...
This expression shows that local packing density makes a significant contribution to expected fluctuations of residues.[6] The terms that follow inverse of the diagonal matrix, are contributions of positional correlations to expected fluctuations.
GNM applications
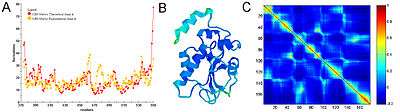
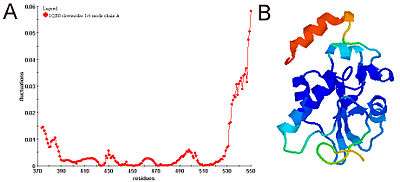
Equilibrium fluctuations
Equilibrium fluctuations of biological molecules can be experimentally measured. In X-ray crystallography β-factor (or temperature factor) of each atom is a measure of mean-squared fluctuation of the native structure. In NMR experiments, this measure can be obtained by calculating root-mean-squared differences between different models. In many applications and publications, including the original articles, it has been shown that expected residue fluctuations obtained from GNM is in good agreement with the experimentally measured native state fluctuations.[7][8] The relation between b-factors, for example, and expected residue fluctuations obtained from GNM is as follows
Figure 3 shows an example of GNM calculation for the catalytic domain of the protein Cdc25B, a cell division cycle dual-specificity phosphatase.
Physical meanings of slow and fast modes
Diagonalization of the Kirchhoff matrix decomposes the normal modes of collective motions of the Gaussian network model of a biomolecule. The expected values of fluctuations and cross-correlations are obtained from linear combinations of fluctuations along these normal modes. The contribution of each mode is scaled with the inverse of that modes frequency. Hence, slow (low frequency) modes contribute most to the expected fluctuations. Along the few slowest modes, motions are shown to be collective and global and potentially relevant to functionality of the biomolecules [9,13,15-18]. Fast (high frequency) modes, on the other hand, describe uncorrelated motions not inducing notable changes in the structure.
Other specific applications
There are several major areas in which the Gaussian network model and other elastic network models are applied and found to be useful.[9] These include:
- Spring bead based network model: In spring-bead based network model, the springs and beads are used as components in the crosslinked network. Springs are cross-linked to represent mechanical behavior of the material and bridge molecular dynamics (MD) model and finite element (FE) model (see Figure. 5). The beads represent material mass of cluster bonds. Each spring is used to represent a cluster of polymer chains, instead of part of a single polymer chain. This simplification allows to bridge different models at multiple length scales and improves the simulation efficiency significantly. At each iteration step in the simulation, forces in the springs are applied to the nodes at the center of the beads, and the equilibrated nodal displacements throughout the system are calculated. Different from the traditional FE method for obtaining stress and strain, the spring–bead model provides the displacements of the nodes and forces in the springs. The equivalent strain and strain energy of spring–bead based network model can be defined and calculated using the displacements of nodes and the spring characteristics. Furthermore, the results from the network model can be scaled up to obtain the structural response at the macroscale using FE analysis.[10][11]
- Decomposition of flexible/rigid regions and domains of proteins [12][13][14]
- Characterization of functional motions and functionally important sites/residues of proteins, enzymes and large macromolecular assemblies [15][16][17][18][19][20][21][22][23][24][25][26]
- Refinement and dynamics of low-resolution structural data, e.g. Cryo-electron microscopy [27][28][29][30]
- Molecular replacement for solving X-ray structures, when a conformational change occurred, with respect to a known structure[31]
- Integration with atomistic models and simulations [32][33]
- Investigation of folding/unfolding pathways and kinetics.[34][35]
- Annotation of functional implication in molecular evolution [36][37]
Web servers
In practice, two kinds of calculations can be performed. The first kind (the GNM per se) makes use of the Kirchhoff matrix.[2][3] The second kind (more specifically called either the Elastic Network Model or the Anisotropic Network Model) makes use of the Hessian matrix associated to the corresponding set of harmonic springs.[1] Both kinds of models can be used online, using the following servers.
GNM servers
- iGNM: A database of protein functional motions based on GNM http://web.archive.org/web/20070623034849/http://ignm.ccbb.pitt.edu/Index.htm
- oGNM: Online calculation of structural dynamics using GNM http://web.archive.org/web/20070516042756/http://ignm.ccbb.pitt.edu:80/GNM_Online_Calculation.htm
- GNM server http://gor.bb.iastate.edu/gnm/gnm.htm
ENM/ANM servers
- Anisotropic Network Model web server http://www.ccbb.pitt.edu/anm [38]
- ANM server http://gor.bb.iastate.edu/anm/anm.htm
- elNemo: Web-interface to The Elastic Network Model http://www.igs.cnrs-mrs.fr/elnemo/
- AD-ENM: Analysis of Dynamics of an Elastic Network Model http://enm.lobos.nih.gov/
- WEBnm@: Web-server for Normal Mode Analysis of proteins http://apps.cbu.uib.no/webnma/home
Other relevant servers
- ProMode: Database of normal mode analysis of proteins http://cube.socs.waseda.ac.jp/pages/jsp/index.jsp
- HingeProt: An algorithm for protein hinge prediction using elastic network models http://www.prc.boun.edu.tr/appserv/prc/hingeprot/, or http://bioinfo3d.cs.tau.ac.il/HingeProt/hingeprot.html
- DNABindProt: A Server for Determination of Potential DNA Binding Sites of Proteins http://www.prc.boun.edu.tr/appserv/prc/dnabindprot/
- MolMovDB: A database of macromolecular motions: http://www.molmovdb.org/
- The Protein Data Bank (PDB) http://www.pdb.org/
- A comprephensive elastic network model server: http://omega.psi.iastate.edu
See also
- Gaussian distribution
- Harmonic oscillator
- Hooke's law
- Molecular dynamics
- Normal mode
- Principal component analysis
- Protein dynamics
- Rubber elasticity
- Statistical mechanics
References
Primary sources
- Direct evaluation of thermal fluctuations in protein using a single parameter harmonic potential, I. Bahar, A. R. Atilgan, and B. Erman Folding & Design 2, 173-181, 1997.
- Gaussian dynamics of folded proteins, Haliloglu, T. Bahar, I. & Erman, B. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 3090-3093, 1997.
- Cui Q, Bahar I, (2006). Normal Mode Analysis: Theory and applications to biological and chemical systems, Chapman & Hall/CRC, London, UK
Specific citations
- 1 2 Tirion, M.M. Large amplitude elastic motions in proteins from a single-parameter, atomic analysis, Phys. Rev. Lett., 77, 1905, 1996.
- 1 2 Direct evaluation of thermal fluctuations in protein using a single parameter harmonic potential, I. Bahar, A. R. Atilgan, and B. Erman Folding & Design 2, 173-181, 1997.
- 1 2 Gaussian dynamics of folded proteins, Haliloglu, T. Bahar, I. & Erman, B. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 3090-3093, 1997.
- ↑ Flory, P.J., Statistical thermodynamics of random networks, Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. A, 351, 351, 1976.
- ↑ Go, N., Noguti, T. and Nishikawa, T. Dynamics of a small globular protein in terms of low-frequency vibrational modes, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 80, 3696, 1983.
- ↑ Halle, B. Flexibility and packing in proteins, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 99, 1274, 2002.
- ↑ Correlation between native state hydrogen exchange and cooperative residue fluctuations from a simple model, I. Bahar, A. Wallqvist, D. G. Covell, & R.L. Jernigan Biochemistry 37, 1067-1075, 1998.
- ↑ Vibrational dynamics of proteins: Significance of slow and fast modes in relation to function and stability, I. Bahar, A. R. Atilgan, M. C. Demirel, & B. Erman, Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 2733-2736, 1998.
- ↑ Chennubhotla C, Rader AJ, Yang LW, Bahar I (2005). Elastic network models for understanding biomolecular machinery: from enzymes to supramolecular assemblies. Phys. Biol. 2:S173-S180 PMID 16280623
- ↑ Zhang, Jinjun (2015). "An optimized cross-linked network model to simulate the linear elastic material response of a smart polymer". Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures. doi:10.1177/1045389X15595292.
- ↑ Zhang, Jinjun (2015). "A novel statistical spring-bead based network model for self-sensing smart polymer materials". Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures. 24 (8): 085022.
- ↑ Analysis of domain motions by approximate normal mode calculations, Hinsen, K, Proteins 33(3), 417-429, 1999
- ↑ Identification of core amino acids stabilizing rhodopsin, Rader, AJ., G. Anderson, B. Isin, H. G. Khorana, I. Bahar, & J. Klein-Seetharaman. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci USA 101: 7246-7251, 2004.
- ↑ Automatic domain decomposition of proteins by a Gaussian Network Model, Kundu, S., Sorensen, D.C., Phillips, G.N. Jr., Proteins 57(4), 725-733, 2004.
- ↑ Zhang, Jinjun (2015). "A novel statistical spring-bead based network model for self-sensing smart polymer materials". Smart Materials and Structures. 24 (8): 085022.
- ↑ Zhang, Jinjun (2015). "An optimized cross-linked network model to simulate the linear elastic material response of a smart polymer". Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures. doi:10.1177/1045389X15595292.
- ↑ Keskin, O. et al. Relating molecular flexibility to function: a case study of tubulin, Biophys. J., 83, 663, 2002.
- ↑ Inhibitor binding alters the directions of domain motions in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, Temiz NA & Bahar I, Proteins: Structure, Function and Genetics 49, 61-70, 2002.
- ↑ Xu, C., Tobi, D. and Bahar, I. Allosteric changes in protein structure computed by a simple mechanical model: hemoglobin T<-> R2 transition, J. Mol. Biol., 333, 153, 2003.
- ↑ Structural Changes Involved in Protein Binding Correlate with intrinsic Motions of Proteins in the Unbound State, Dror Tobi & Ivet Bahar. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 102, 18908-18913, 2005.
- ↑ Common Mechanism of Pore Opening Shared by Five Different Potassium Channels, Indira H. Shrivastava & Ivet Bahar. Biophys J 90, 3929-3940, 2006.
- ↑ Yang LW, Bahar I (2005). Coupling between Catalytic Site and Collective Dynamics: A requirement for Mechanochemical Activity of Enzymes. Structure 13:893-904 doi:10.1016/j.str.2005.03.015 PMID 15939021
- ↑ Markov Methods for Hierarchical Coarse-Graining of Large Protein Dynamics, Chakra Chennubhotla & Ivet Bahar. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 3909, 379-393, 2006.
- ↑ Global Ribosome Motions Revealed with Elastic Network Model, Wang, Y. Rader, AJ, Bahar, I. & Jernigan, RL. , J. Struct Biol 147: 302-314, 2004.
- ↑ Maturation Dynamics of Bacteriophage HK97 Capsid, AJ Rader, Daniel Vlad & Ivet Bahar. Structure (Camb) 13:413-21, 2005.
- ↑ Hamacher, K., Trylska, J., McCammon, J.A. Dependency Map of Proteins in the Small Ribosomal Subunit. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2(2): e10, 2006
- ↑ Ming, D. et al. How to describe protein motion without amino acid sequence and atomic coordinates, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 99, 8620, 2002.
- ↑ Tama, F., Wriggers, W. and Brooks III, C.L. Exploring global distortions of biological macromolecules and assemblies from low-resolution structural information and elastic network theory, J. Mol. Biol., 321, 297, 2002.
- ↑ Delarue, M. and Dumas, P. On the use of low-frequency normal modes to enforce collective movements in refining macromolecular structural models, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 101, 6957, 2004.
- ↑ Micheletti, C., Carloni, P. and Maritan, A. Accurate and efficient description of protein vibrational dynamics: comparing molecular dynamics and gaussian models, Proteins, 55, 635, 2004.
- ↑ Suhre, K. and Sanejouand, Y.H. On the potential of normal mode analysis for solving difficult molecular replacement problems, Acta Crystallogr. D 60, 796, 2004.
- ↑ Zhang, Z.Y., Shi, Y.Y. and Liu, H.Y. Molecular dynamics simulations of peptides and proteins with amplified collective motions, Bipohys. J., 84, 3583, 2003.
- ↑ Micheletti, C., Lattanzi, G. and Maritan, A. Elastic properties of proteins: insight on the folding process and evolutionary selection of native structures, J. Mol. Biol., 321, 909, 2002.
- ↑ Micheletti, C. et al. Crucial stages of protein folding through a solvable model: predicting target sites for enzyme-inhibiting drugs, Prot. Sci., 11, 1878, 2002.
- ↑ Portman, J.J., Takada, S. and Wolynes, P.G. Microscopic theory of protein folding rates. I. fine structure of the free energy profile and folding routes from a variational approach, J. Chem. Phys., 114, 5069, 2001.
- ↑ Hamacher, K. Relating Sequence Evolution of HIV1-Protease to Its Underlying Molecular Mechanics, Gene, 422, 30-36, 2008.
- ↑ Hamacher, K., McCammon J.A. Computing the amino acid specificity of fluctuations in biomolecular systems, J.Chem.Theo.Comp. 2:873, 2006.
- ↑ Anisotropy of fluctuation dynamics of proteins with an elastic network model, Atilgan, AR, Durrell, SR, Jernigan, RL, Demirel, MC, Keskin, O. & Bahar, I. Biophys. J. 80, 505-515, 2001.