Emperor Go-Uda
| Go-Uda | |
|---|---|
| Emperor of Japan | |
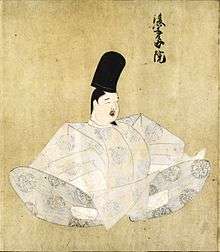 Go-Uda | |
| Reign | 1274–1287 |
| Predecessor | Kameyama |
| Successor | Fushimi |
| Born | December 17, 1267 |
| Died | July 16, 1324 (aged 56) |
| Burial | Rengebu-ji no Misasagi (Kyoto) |
Emperor Go-Uda (後宇多天皇 Go-Uda-tennō) (December 17, 1267 – July 16, 1324) was the 91st emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession. His reign spanned the years from 1274 through 1287.[1]
This 13th-century sovereign was named after the 9th-century Emperor Uda and go- (後), translates literally as "later"; and thus, he is sometimes called the "Later Emperor Uda," or, in some older sources, may be identified as "Emperor Uda, the second" or as "Emperor Uda II."
Genealogy
Before his ascension to the Chrysanthemum Throne, his personal name (imina) was Yohito (世仁).[2]
He was the second son of Emperor Kameyama. They were from the Daikakuji line.
- Consort: Horikawa (Minamoto) Motoko (堀河(源)基子)
- First son: Imperial Prince Kuniharu (邦治親王) (Emperor Go-Nijō)
- Consort: Itsutsuji (Fujiwara) ?? (五辻(藤原)忠子)
- Second daughter: Imperial Princess ?? (禖子内親王)
- Second son: Imperial Prince ?? (尊治親王) (Emperor Go-Daigo)
- Third son: Prince ?? (性円法親王) (Buddhist Priest)
- Fourth son: Prince ?? (承覚法親王) (Buddhist Priest)
- Consort: Princess ?? (揄子女王)
- First daughter: Imperial Princess ?? (愉子内親王)
Events of Go-Uda's life
Yohito-shinnō became crown prince in 1268. According to the terms of the late emperor's will (Go-Saga died in 1272), in 1274, he would become emperor upon the death or abdication of Emperor Kameyama.
- 1274 (Bun'ei 11, 1st month): In the 15th year of Kameyama-tennō 's reign (亀山天皇十五年), the emperor abdicated; and the succession (senso) was received by his cousin.[3]
- 1274 (Bun'ei 11, 3rd month): Emperor Go-Uda is said to have acceded to the throne (sokui).[4]
The retired Emperor Kameyama continued to exercise power as cloistered emperor.
During his reign, the unsuccessful Mongol invasions of Japan occurred, first in 1274 and again in 1281. Though they established a beachhead at Hakata, Kyushu, they were driven out within a short time.
- 1275 (Bun'ei 11, 10th month): Hirohito-shinnō was named Crown Prince and heir to his first cousin, the Daikakuji-tō Emperor Go-Uda. This was the result of political maeuvering by Hirohito's father, the Jimyōin-tō Emperor Go-Fukakusa.[5]
In 1287, retired Emperor Go-Fukakusa, dissatisfied with the fact that his own lineage (the Jimyōin-tō) did not control the throne, while that of his younger brother, the retired Emperor Kameyama (the Daikakuji-tō) did, persuaded both the Bakufu and the imperial court to compel the Emperor to abdicate in favor of Go-Fukakusa's son (Emperor Fushimi).
After this time, the struggle between the Jimyōin-tō and the Daikakuji-tō over the imperial throne continued. After Go-Uda's abdication, his Daikakuji-tō controlled the throne from 1301 to 1308 (Emperor Go-Nijō) and again from 1318 until the era of northern and southern courts (begun 1332) when they became the southern court (ending in 1392).
Go-Uda was cloistered emperor during the reign of his own son, Go-Nijō, from 1301 until 1308, and again from 1318, when his second son Go-Daigo took the throne until 1321, when Go-Daigo began direct rule.

Emperor Go-Uda's Imperial mausoleum is the Rengebuji no misasagi (蓮華峯寺陵) in Ukyō-ku, Kyoto.[7]
Kugyō
Kugyō (公卿) is a collective term for the very few most powerful men attached to the court of the Emperor of Japan in pre-Meiji eras. Even during those years in which the court's actual influence outside the palace walls was minimal, the hierarchic organization persisted.
In general, this elite group included only three to four men at a time. These were hereditary courtiers whose experience and background would have brought them to the pinnacle of a life's career. During Go-Uda's reign, this apex of the Daijō-kan included:
- Sesshō, Kujō Tadaie, 1274
- Sesshō, Ichijō Ietsune, 1274–1275
- Sesshō, Takatsukasa Kanehira, 1275–1278
- Kampaku, Takatsukasa Kanehira, 1278–1287
- Kampaku, Nijō Morotada, 1287–1289
- Sadaijin
- Udaijin
- Nadaijin
- Dainagon
Eras of Go-Uda's reign
The years of Go-Uda's reign are more specifically identified by more than one era name or nengō.[8]
Notes
- ↑ Titsingh, Isaac. (1834). Annales des empereurs du Japon, pp. 262–268; Varley, H. Paul. (1980). Jinnō Shōtōki. pp. 233–237.
- ↑ Titsingh, p. 262; Varley, p. 233.
- ↑ Titsingh, p. 261; Varley, p. 44; a distinct act of senso is unrecognized prior to Emperor Tenji; and all sovereigns except Jitō, Yōzei, Go-Toba, and Fushimi have senso and sokui in the same year until the reign of Emperor Go-Murakami.
- ↑ Titsingh, p. 262; Varley, p. 44.
- ↑ Titsingh, p. 262, 270.
- ↑ Varley, p. 237.
- ↑ Ponsonby-Fane, Richard. (1959). The Imperial House of Japan, p. 422.
- ↑ Titsingh, p. 262.
See also
References
- Ponsonby-Fane, Richard Arthur Brabazon. (1959). The Imperial House of Japan. Kyoto: Ponsonby Memorial Society. OCLC 194887
- Titsingh, Isaac. (1834). Nihon Odai Ichiran; ou, Annales des empereurs du Japon. Paris: Royal Asiatic Society, Oriental Translation Fund of Great Britain and Ireland. OCLC 5850691
- Varley, H. Paul. (1980). Jinnō Shōtōki: A Chronicle of Gods and Sovereigns. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-04940-5; OCLC 5914584
External links
- Kyoto National Museum – "Treasures of Daikaku-ji," including portrait of Go-Uda and the former-emperor's will
| Regnal titles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Emperor Kameyama |
Emperor of Japan: Go-Uda 1274–1287 |
Succeeded by Emperor Fushimi |
