Treaty of Greenville
1805 map showing western "Indian Boundary" between Port William and Fort Recovery, as well as the northern "Gen Wayne Treaty 1793" boundary between Fort Recovery and the Muskingum River near Salem. Much of the land east and south of these boundaries was open to settlement after the Treaty of Greenville.


The Treaty of Greenville was signed on August 3, 1795, at Fort Greenville, now Greenville, Ohio; it followed negotiations after the Native American loss at the Battle of Fallen Timbers a year earlier. It ended the Northwest Indian War in the Ohio Country and limited strategic parcels of land to the north and west. The parties to the treaty were a coalition of Native American tribes, known as the Western Confederacy, and United States government represented by General Anthony Wayne for local frontiersmen. The treaty is considered "the beginning of modern Ohio history."[1]
The treaty established what became known as the Greenville Treaty Line, which was for several years a boundary between Native American territory and lands open to European-American settlers. The latter frequently disregarded the treaty line as they continued to encroach on Native American lands.
The treaty also established the "annuity" system: yearly grants of federal money and supplies of calico cloth to Native American tribes and thus institutionalized continuing government influence in tribal affairs, giving outsiders considerable control over Native American life.[2]
Details
In exchange for goods to the value of $20,000 (such as blankets, utensils, and domestic animals), the Native American tribes ceded to the United States large parts of modern-day Ohio, the future site of downtown Chicago,[nb 1][4] the Fort Detroit area, Maumee, Ohio Area,[5] and the Lower Sandusky Ohio Area.[6]
The United States was represented by General "Mad Anthony" Wayne, who led the victory at Fallen Timbers. Other Americans at the treaty include William Wells, William Henry Harrison, William Clark, Caleb Swan, and Meriwether Lewis.[7]
Native American leaders who signed the treaty included leaders of these bands and tribes: Wyandot Chiefs Tarhe , Leatherlips, Roundhead (Wyandot), Delaware (Lenape; several bands). Shawnee, Chief Blue Jacket, Ottawa (several bands), Chippewa, Potawatomi (several bands), Miami (several bands), Chief Little Turtle, Wea, Kickapoo, and Kaskaskia.[8]
History
William Clark of the Lewis and Clark Expedition was present at Greenville. Years later he met again one of the Delaware chiefs from the conference, and noted in his journal for December 23, 1803: "a raney [sic] day… several Deleaway pass, a chief whome I saw at Greenville Treaty, I gave him a bottle of whiskey."[9]
Nearly twenty years later, on July 22, 1814 General William Henry Harrison and Governor Lewis Cass held a second treaty signing at Greenville, with the Wyandot, Delaware, Shawnee, Seneca, Miami and Potawatomi tribes.[10] That treaty brought support from those tribes for the US during the War of 1812.
Treaty line route
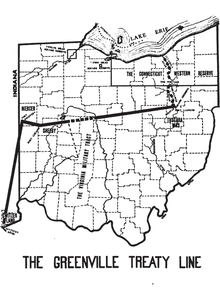
The treaty line began at the mouth of the Cuyahoga River in present-day Cleveland and ran south along the river to the portage between the Cuyahoga and Tuscarawas River, in what is now known as the Portage Lakes area between Akron and Canton. The line continued down the Tuscarawas to Fort Laurens near present-day Bolivar. From there, the line ran west-southwest to near present-day Fort Loramie on a branch of the Great Miami River. From there, the line ran west-northwest to Fort Recovery, on the Wabash River near the present-day boundary between Ohio and Indiana. From Fort Recovery, the line ran south-southwest to the Ohio River at a point opposite the mouth of the Kentucky River in present-day Carrollton, Kentucky.
Depictions
A painting commemorating the treaty hangs in the Ohio Statehouse. It was completed by the Ohio artist Howard Chandler Christy. At 23 feet wide, it is the largest painting in the Ohio Statehouse.[11]
Gallery
Notes
References
- ↑ "Capitol Ohio : 113 - Treaty of Greenville". The Ohio Statehouse. Retrieved 2015-09-13.
- ↑ Eric Foner, Give Me Liberty
- ↑ Charles J. Kappler (1904). "TREATY WITH THE WYANDOT, ETC., 1795". U.S. Government treaties with American Indian tribes. Oklahoma State University Library. Retrieved 1 August 2009.
- ↑ "Fort Dearborn" in online Encyclopedia of Chicago accessed 2009-08-01
- ↑ see Article 3 #8
- ↑ see Article 3 #11
- ↑ "Capitol Ohio : 113 - Treaty of Greenville". The Ohio Statehouse. Retrieved 2015-09-13.
- ↑ "Capitol Ohio : 113 - Treaty of Greenville". The Ohio Statehouse. Retrieved 2015-09-13.
- ↑ G. Moulton, ed. The Journals of the Lewis and Clark Expedition. Vol. 2, p. 140.
- ↑
- ↑ "Capitol Ohio : 113 - Treaty of Greenville". The Ohio Statehouse. Retrieved 2015-09-13.
External links
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Treaty of Greenville. |
Coordinates: 40°06′28″N 84°37′54″W / 40.1078°N 84.6316°W
.jpg)



