Hellenic Trench
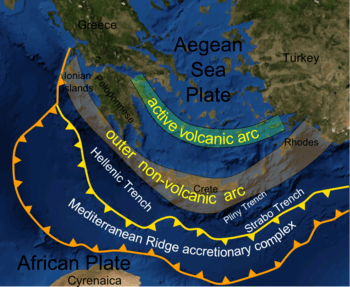
The Hellenic Trench is a hemispherical-scale long narrow depression in the Ionian Sea.
The hadal zone of the Hellenic trench is roughly 4,150 metres (13,615 feet) to 5,300 metres (17,388 feet) deep. The names of the three major parts of the Hellenic trench are: Matapan Deep System or Matapan–Vavilov Deep, roughly 5,120 meters (16,797 feet), the Kithera–Antikithera System, 4,615 metres (15,141 feet), and the Zakinthos–Strofadhes system, 4,150 metres (13,615 feet).
The Calypso Deep, located in the Hellenic Trench, is roughly 5,267 metres (17,280 feet) deep and is the deepest point in the Mediterranean Sea.
The region of the Hellenic trench is an ecosystem to sperm whales and other aquatic life. The trench has been used by marine biologists to study the behaviour of various aquatic species.
This is the trench where several earthquakes, including the 365 Crete earthquake, occurred.
See also
References
- C. Blanpied, D.J. Stanley 1981. "Uniform Mud(unifite) Deposition in the Hellenic Trench Eastern Mediterranean". Smithsonian Contributions to the Marine Sciences Number 13. Smithsonian Institution Press, 5p.