Heteropoly acid
A heteropoly acid is a class of acid made up of a particular combination of hydrogen and oxygen with certain metals and non-metals. This type of acid is a common re-usable acid catalyst in chemical reactions.[1]
To qualify as a heteropoly acid, the compound must contain:
- a metal such as tungsten, molybdenum or vanadium, termed the addenda atom;
- oxygen;
- an element generally from the p-block of the periodic table, such as silicon, phosphorus or arsenic, termed the hetero atom;
- acidic hydrogen atoms.
The metal addenda atoms linked by oxygen atoms form a cluster with the hetero-atom inside bonded via oxygen atoms. Examples with more than one type of metal addenda atom in the cluster are well known. The conjugate anion of a heteropoly acid is known as a polyoxometalate.
Due to the possibilities of there being different combinations of addenda atoms and different types of hetero atoms there are a lot of heteropolyacids. Two of the better known groups of these are based on the Keggin, HnXM12O40, and Dawson, HnX2M18O62, structures.
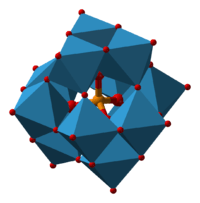 |
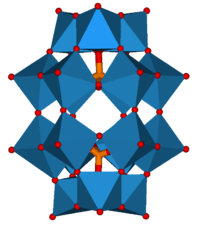 |
| Keggin structure, XM12O40n− | Dawson structure, X2M18O62n− |
Some examples are:
- H4Xn+M12O40, X = Si, Ge; M = Mo, W
- H3Xn+M12O40, X = P, As; M = Mo, W
- H6X2M18O62, X=P, As; M = Mo, W
The heteropolyacids are widely used as homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts,[2] particularly those based on the Keggin structure as they can possess qualities such as good thermal stability, high acidity and high oxidising ability. Some examples of catalysis are:[3]
- Homogeneous acid catalysis
- hydrolysis of propene to give propan-2-ol by H3PMo12O40 and H3PW12O40
- Prins reaction by H3PW12O40
- polymerisation of THF by H3PW12O40
- Heterogeneous acid catalysis
- dehydration of propan-2-ol to propene and methanol to hydrocarbons by H3PW12O40
- reformation of hexane to 2-methylpentane (isohexane) by H3PW12O40 on SiO2
- Homogeneous oxidation
- cyclohexene + H2O2 to adipic acid by the mixed addenda H3PMo6V6O40
- ketone by O2 to acid and aldehyde by mixed addenda H5PMo10V2O40
Heteropolyacids have long been used in analysis and histology and are a component of many reagents e.g. the Folin-Ciocalteu reagent, folins phenol reagent used in the Lowry protein assay and EPTA, ethanolic phosphotungstic acid.
See also
Notes
- ↑ Mizuno, Noritaka; Misono, Makoto (1998). "Heterogeneous Catalysis". Chemical Reviews. 98: 199–217. doi:10.1021/cr960401q.
- ↑ Kozhevnikov, I. V. (1998). "Catalysis by heteropoly acids and multicomponent polyoxometalates in liquid-phase reactions". Chemical Reviews. 98 (1): 171–198. doi:10.1021/cr960400y. PMID 11851502.
- ↑ "Oxide catalysts in solid state chemistry". T Okuhara, M Misono. Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry. Editor R Bruce King (1994). John Wiley and Sons. ISBN 0-471-93620-0
References
Cotton, F. Albert; Wilkinson, Geoffrey; Murillo, Carlos A.; Bochmann, Manfred (1999), Advanced Inorganic Chemistry (6th ed.), New York: Wiley-Interscience, ISBN 0-471-19957-5