Hill of Howth Tramway

The Howth Tram was a tram which served Howth Head, near Dublin, Ireland. The termini were at Sutton railway station and Howth railway station. It operated from June 1901 to 31 May 1959 and was run by the Great Northern Railway (Ireland) (GNR(I)), which viewed it as a way to bring more customers to its railway stations at Sutton and Howth.
History
Closure and replacement

In 1958, Córas Iompair Éireann (CIÉ) took over GNR(I)'s operations in the Republic of Ireland, including the Howth Tram. A year later, the tramway was closed down. It was initially replaced by two CIÉ bus routes – numbers 87 (Sutton to Ceanchor Road) and 88 (Howth to Windgate Road).[1] Two routes were necessary, as several narrow hill curves were not passable by the buses used. Eventually, sections of the disused tram route between the Baily post office and the Summit were converted to a wider road and a single bus route (number 88) was possible.
The area is now served by the 31, 31a and 31b bus routes which operate from Abbey Street in the city centre. In winter, icy roads on the hill occasionally cause the bus service to be suspended, unlike the tram, which ran in all weather conditions.
Preservation
.jpg)

Four of the trams survive in preservation. No. 9 is now exhibited at the National Transport Museum of Ireland, which is located at Howth Castle, near the former terminus of the tramway at Howth railway station.[2] No. 4 is on display the Ulster Folk and Transport Museum at Cultra. No. 10 is preserved at the National Tramway Museum in Derbyshire, England; it has been converted to 4' 8.5" gauge and had previously run on the Blackpool Tramway from 1985-89.[3][4] No. 2 is at the Orange Empire Railway Museum, California, USA, in operating condition; it has also been converted to 4' 8.5" gauge.[5]
Plans to Reinstate the Tram
In 2016 Fingal County Council announced it was issuing an invitation of tenders[6] for options for possible reinstatement of the Howth Tram or part of it, as a possible tourist attraction.[7][8] Proposals which are being considered include the possibility of having a horse drawn tram on tracks along the seafront.[9]
Route
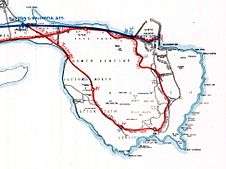
Electric double-decker tramcars ran the five-mile route, which went from Sutton station along Greenfield Road and Carrickbrack Road to St. Fintan's Cemetery, then past the Baily post office and Stella Maris convent to Howth Summit. From there, the tramway ran down into Howth, terminating at the railway station. Most of the route was single track, with passing points at the main stopping places. The track gauge was 1,600 mm (5 ft 3 in), the same standard as railways in Ireland.
Stops
| Stop | Year opened | Year closed | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sutton Station[10] | 1901 | 1959 | Sutton tramcar shed (connected to mainline in 1951)[10] |
| Sutton Cross[10] | 1901 | 1959 | |
| Marine Hotel[10] | 1901 | 1959 | Request stop[10] |
| Church Road[10] | 1901 | 1959 | Request stop. Formerly called Saxe (or Sax or Sacks) Lane[10] |
| Strand Road[10] | 1901 | 1959 | |
| Howth Desmesne[10] | 1901 | 1959 | |
| St Fintans' Cemetery[10] | 1901 | 1959 | Request stop[10] |
| St Fintans[10] | 1901 | 1959 | |
| St Fintans' Road[10] | 1901 | 1959 | Request stop[10] |
| Barren Hill[10] | 1901 | 1959 | |
| Red Rock[10] | 1901 | 1959 | Request stop[10] |
| Somali Village[10] | 1901 | 1959 | Request stop (also called Bellinghams')[10] |
| Ceanchor Road[10] | 1901 | 1959 | Request stop[10] |
| Baily Post Office[10] | 1901 | 1959 | |
| Convent Gate[10] | 1901 | 1959 | Request stop[10] |
| Stella Maris[10] | 1901 | 1959 | Formerly called Bay View or Baily View[10] |
| Ravensdale[10] | 1901 | 1959 | Request stop[10] |
| Tweedys' Lane[10] | 1901 | 1959 | Request stop[10] |
| Hill of Howth[10] | 1901 | 1959 | Formerly called Howth Summit, renamed 1912[10] |
| Kitestown Road[10] | 1901 | 1959 | Request stop (formerly called Bakers' Lane)[10] |
| Greys' Lane[10] | 1901 | 1959 | Request stop[10] |
| Dungriffen Road[10] | 1901 | 1959 | |
| Balkill Road[10] | 1901 | 1959 | Request stop (also called Balglass)[10] |
| Island View[10] | 1901 | 1959 | Request stop[10] |
| 'Korea'[10] | circa 1950s | 1959 | Unofficial stopping place[10] |
| Howth Station[10] | 1901 | 1959 | Connection to mainline[10] |
See also
- Dublin United Transport Company - The largest tramway operator in Dublin (pre-1945)
- Clontarf and Hill of Howth Tramroad
- Dublin and Blessington Steam Tramway
- Dublin tram system
References
- ↑ "Hill Of Howth Tramway Closure". Irish Railfans' News. Railway Preservation Society of Ireland. 5 (3): 6. July 1959.
- ↑ "The Hill of Howth Tramway and tram No. 9". www.nationaltransportmuseum.org. Retrieved 2016-05-02.
- ↑ "GNRi Hill of Howth Tram No.10". www.irishrailwaymodelling.com. Retrieved 2016-05-02.
- ↑ "Blackpooltra.ms". www.tramway.com. Retrieved 2016-05-02.
- ↑ "Trams DownUnder - Message 179538". tdu.to. Retrieved 2016-05-02.
- ↑ Feasibility study on reinstatement of Howth Tram Mytenders.ie, 15 June 2016.
- ↑ Ding Ding Old Number 9 tram may roll again in Howth by Dan Griffin, Irish Times, June 16, 2016
- ↑ FINGAL COUNTY COUNCIL CONSIDERING RESTORING HOWTH TRAM Interview with FIngal County Council Mayor, www.q102.ie, 20 June 2016.
- ↑ Howth tram is on course to be running again by Tom Prenderville, Irish Independent, 15 July 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 Johnson, Stephen (1997). Johnson's Atlas & Gazetteer of the railways of Ireland. Leicester,UK: Midland Publishing. ISBN 1-85780-044-3.
Further reading
- Kilroy, James: Howth and her Trams: Stories and Sketches of the Howth Tram, Fingal Books, Dublin (1986). ISBN 978-1-85186-010-4
- Kilroy, James: Trams to the Hill of Howth: A Photographic Tribute, Colourpoint Books, Newtownards, Co. Down (1998) ISBN 1-898392-13-7, ISBN 978-1-898392-13-2