Hinged dissection
A hinged dissection, also known as a swing-hinged dissection or Dudeney dissection,[1] is a kind of geometric dissection in which all of the pieces are connected into a chain by "hinged" points, such that the rearrangement from one figure to another can be carried out by swinging the chain continuously, without severing any of the connections.[2] Typically, it is assumed that the pieces are allowed to overlap in the folding and unfolding process;[3] this is sometimes called the "wobbly-hinged" model of hinged dissection.[4]
History

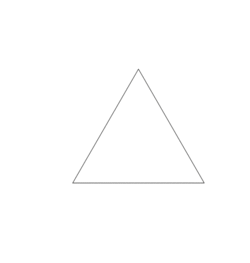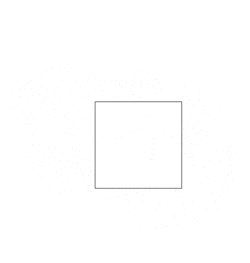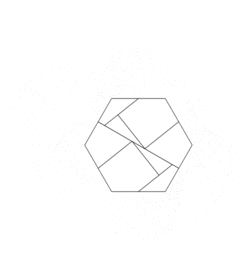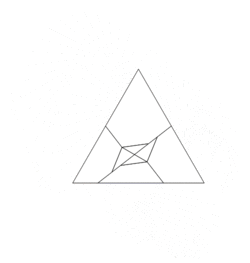
The concept of hinged dissections was popularised by the author of mathematical puzzles, Henry Dudeney. He introduced the famous hinged dissection of a square into a triangle (pictured) in his 1907 book The Canterbury Puzzles.[5] The Wallace–Bolyai–Gerwien theorem, first proven in 1807, states than any two equal-area polygons must have a common dissection. However, the question of whether two such polygons must also share a hinged dissection remained open until 2007, when Erik Demaine et al. proved that there must always exist such a hinged dissection, and provided a constructive algorithm to produce them.[4][6][7] This proof holds even under the assumption that the pieces may not overlap while swinging, and can be generalised to any pair of three-dimensional figures which have a common dissection (see Hilbert's third problem).[6][8] In three dimensions, however, the pieces are not guaranteed to swing without overlap.[9]
Other hinges
Other types of "hinges" have been considered in the context of dissections. A twist-hinge dissection is one which use a three-dimensional "hinge" which is placed on the edges of pieces rather than their vertices, allowing them to be "flipped" three-dimensionally.[10][11] As of 2002, the question of whether any two polygons must have a common twist-hinged dissection remains unsolved.[12]
References
- ↑ Akiyama, Jin; Nakamura, Gisaku (2000). "Dudeney Dissections of Polygons". Discrete and Computational Geometry. 1763: 14–29. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-46515-7_2.
- ↑ Pitici, Mircea (September 2008). "Hinged Dissections". Math Explorers Club. Cornell University. Retrieved 19 December 2013.
- ↑ O'Rourke, Joseph (2003). "Computational Geometry Column 44". arXiv:cs/0304025v1
 [cs.CG].
[cs.CG]. - 1 2 "Problem 47: Hinged Dissections". The Open Problems Project. Smith College. 8 December 2012. Retrieved 19 December 2013.
- ↑ Frederickson 2002, p.1
- 1 2 Abbot, Timothy G.; Abel, Zachary; Charlton, David; Demaine, Erik D.; Demaine, Martin L.; Kominers, Scott D. "Hinged Dissections Exist". arXiv:0712.2094
 . doi:10.1145/1377676.1377695.
. doi:10.1145/1377676.1377695. - ↑ Bellos, Alex (30 May 2008). "The science of fun". The Guardian. Retrieved 20 December 2013.
- ↑ Phillips, Tony (November 2008). "Tony Phillips' Take on Math in the Media". Math in the Media. American Mathematical Society. Retrieved 20 December 2013.
- ↑ O'Rourke, Joseph (March 2008). "Computational Geometry Column 50" (PDF). ACM SIGACT News. ACM. 39 (1). Retrieved 20 December 2013.
- ↑ Frederickson 2002, p.6
- ↑ Frederickson, Greg N. (2007). Symmetry and Structure in Twist-Hinged Dissections of Polygonal Rings and Polygonal Anti-Rings (PDF). Bridges 2007. The Bridges Organization. Retrieved 20 December 2013.
- ↑ Frederickson 2002, p. 7
Bibliography
- Frederickson, Greg N. (26 August 2002). Hinged Dissections: Swinging and Twisting. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521811929. Retrieved 19 December 2013.