iMac G5
|
The original iMac G5 with an Apple Wireless Mouse. | |
| Developer | Apple Inc. |
|---|---|
| Type | Desktop |
| Release date |
August 31, 2004 (original models) May 3, 2005 (Ambient Light Sensor model) October 12, 2005 (iSight model) |
| Discontinued |
January 10, 2006 (17" model) March 20, 2006 (20" model) |
| CPU | PowerPC G5, 1.6–2.1 GHz |
| Predecessor | iMac G4 |
| Successor | Intel iMac |
| Website | www.apple.com/imac/ at the Wayback Machine (archived September 1, 2004) |
The iMac G5 is an all-in-one desktop computer designed and built by Apple Inc. from 2004 to 2006. It was the final iMac to use a PowerPC processor, making it the last model that could natively run Mac OS 9 (Classic) applications. It was replaced in 2006 by the Intel iMac.
History
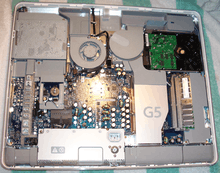
In August 2004, the iMac design was overhauled. By this time, the PowerPC 970 processor had been released and was being used in the Power Mac G5 line. Famously, the Power Mac G5 needed multiple fans in a large casing because of the high heat output from the PowerPC 970.
Apple's new iMac managed to incorporate the PowerPC 970 into an all-in-one design with a distinctive form factor. The computer used the same 17 and 20-inch widescreen LCDs found in the iMac G4, with the main logic board and optical drive now mounted directly behind the LCD panel; this gave the appearance of a thickened desktop LCD monitor. The approximately two inches deep enclosure is suspended above the desk by an aluminum arm that can be replaced by a VESA mounting plate. The iMac G5 uses an advanced cooling system controlled by the operating system; at low CPU loads this rendered the iMac G5 virtually silent. Apple boasted that it was the slimmest desktop computer on the market.
The iMac G5 was updated in March 2005 to the Ambient Light Sensor (ALS) revision. It included a handful of configuration differences - more RAM, a larger hard drive, improved graphics, Gigabit Ethernet, and standard AirPort Extreme (802.11g) and Bluetooth 2.0+EDR.
In October 2005, the final revision was released, adding an integrated iSight webcam mounted above the LCD and Apple's Front Row media interface. Other improvements included faster processors, more RAM, larger hard drives, and improved graphics. Notably this became the first Apple computer to use the PCI Express expansion bus and DDR2 SDRAM, with these features appearing shortly before they were incorporated into the Power Mac G5. It was declared "The Gold Standard of desktop PCs" by Walt Mossberg of the Wall Street Journal.[1]
Although the iMac G5 iSight looked outwardly similar to the two previous revisions, it had a slimmer, internally new design. Improvements included superior cooling and performance increases. The stand could no longer be replaced with a VESA mount. This case, unlike the previous models, opened only from the front and requires the LCD screen to be removed before internal components can be accessed. Apple recommend no user serviceable items other than RAM, which is accessible through a small door at the base of the housing. In the intervening years, many guides have been posted on the internet to support replacing other components including the hard drive and optical drive, though doing so voids any remaining Apple warranty.
The iMac G5 was succeeded by the Intel-based iMac on January 10, 2006, beginning the 6-month transition of Apple's entire line of computers to the Intel architecture.
Revision history
| Component | iMac G5 (August 2004) | iMac G5 Ambient Light Sensor (May 2005) | iMac G5 iSight (October 2005) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Codename | "Hero"[2] | "Q45C", "Q45D" | "Q87" | ||||
| Model identifier | PowerMac8,1 | PowerMac8,2 | PowerMac12,1 | ||||
| Enclosure | White polycarbonate | ||||||
| Display | 17", 1440 × 900 | 20", 1680 × 1050 | 17", 1440 × 900 | 20", 1680 × 1050 | 17", 1440 × 900 | 20", 1680 × 1050 | |
| widescreen 16:10, matte display | |||||||
| Processor | 1.6 or 1.8 GHz | 1.8 GHz | 1.8 or 2.0 GHz | 2.0 GHz | 1.9 GHz | 2.1 GHz | |
| PowerPC G5 970fx | |||||||
| Cache | 64 KB (instruction), 32 KB (data) L1, 512 KB L2 (1:1) | ||||||
| Front side bus | 533 MHz or 600 MHz (3:1) | 600 MHz or 667 MHz (3:1) | 633 MHz (3:1) | 700 MHz (3:1) | |||
| Memory | 256 MB of 400 MHz PC-3200 DDR SDRAM Expandable to 2 GB |
512 MB of 533 MHz PC2-4200 DDR2 SDRAM Expandable to 2.5 GB | |||||
| Graphics | nVidia GeForce FX 5200 Ultra graphics processor with 64 MB of DDR SDRAM nVidia GeForce 4 MX graphics processor with 32 MB of DDR SDRAM (Education Only) |
ATI Radeon 9600 graphics processor with 128 MB of DDR SDRAM | ATI Radeon X600 Pro with 128 MB of DDR SDRAM | ATI Radeon X600 XT with 128 MB of DDR SDRAM | |||
| AGP 8x | PCI Express | ||||||
| Hard drive | 80 GB | 160 GB | 160 GB | 250 GB | 160 GB Optional: 250 or 500 GB | 250 GB Optional: 500 GB | |
| Serial ATA 7200-rpm | |||||||
| Optical drive Slot-loading |
CD-RW/DVD-ROM Combo drive (1.6 GHz) CD-RW/DVD-R SuperDrive (1.8 GHz) | CD-RW/DVD-R SuperDrive | CD-RW/DVD-ROM Combo drive (1.8 GHz) CD-RW/DVD-RW DL SuperDrive (2.0 GHz) | CD-RW/DVD-RW DL SuperDrive | CD-RW/DVD-R DL 8x SuperDrive | ||
| Connectivity | Optional AirPort Extreme 802.11b/g 10/100BASE-T Ethernet 56k V.92 Modem Optional Bluetooth 1.1 | Integrated Airport Extreme 802.11b/g Gigabit Ethernet 56k Modem Bluetooth 2.0+EDR | Integrated Airport Extreme 802.11b/g Gigabit Ethernet Optional 56k V.92 USB modem Bluetooth 2.0+EDR Built-in infrared (IR) receiver for Apple Remote | ||||
| Peripherals | 3x USB 2.0 2x Firewire 400 Audio input/audio output | 3x USB 2.0 2x Firewire 400 Audio input/audio output Ambient Light Sensor | 3x USB 2.0 2x Firewire 400 Audio input/audio output Ambient Light Sensor | ||||
| Camera | None Optional External iSight Camera (640 × 480 0.3 MP) | Integrated iSight Camera (640 × 480 0.3 MP) | |||||
| Video out | Mini-VGA | ||||||
| Original Operating System | Mac OS X 10.3 "Panther" | Mac OS X 10.4 "Tiger" | |||||
| Maximum Operating System | Mac OS X 10.5.8 "Leopard" | ||||||
| Weight | 18.5 lb / 8.4 kg (17"), 25.2 lb / 11.4 kg (20") | 15.5 lb / 7 kg (17"), 22 lb / 10 kg (20") | |||||
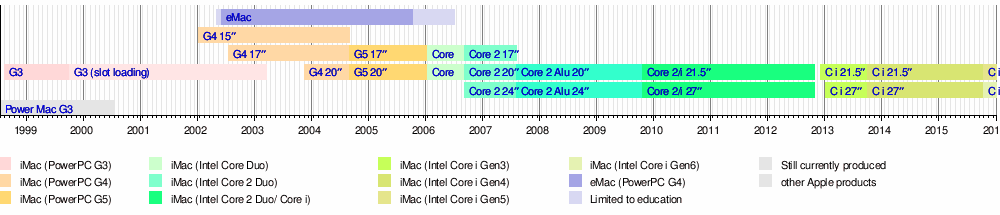
Timeline of iMac models
See also
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to IMac G5. |
- ↑ , The Mossberg Solution, November 30, 2005.
- ↑ "Apple Unveils the New iMac G5".
| Preceded by iMac G4 |
iMac G5 August 31, 2004 |
Succeeded by iMac (Intel-based) |
