International Linear Collider
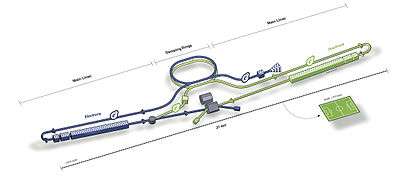
The International Linear Collider (ILC) is a proposed linear particle accelerator.[1] It is planned to have a collision energy of 500 GeV initially, with the possibility for a later upgrade to 1000 GeV (1 TeV). The host country for the accelerator has not yet been chosen and proposed locations are Japan, Europe (CERN) and the USA (Fermilab).[2] Japan is considered the most likely candidate, as the Japanese government is willing to contribute half of the costs, according to the coordinator of study for detectors at the ILC.[3]
Studies for an alternative project called the Compact Linear Collider (CLIC) are also underway, which would operate at higher energies (up to 3 TeV) in a machine of length similar to the ILC.
The ILC would collide electrons with positrons. It will be between 30 km and 50 km (19–31 mi) long, more than 10 times as long as the 50 GeV Stanford Linear Accelerator, the longest existing linear particle accelerator. The proposal is based on previous similar proposals from Europe, the U.S., and Japan.
Comparison with LHC
There are two basic shapes of accelerators. Linear accelerators ("linacs") accelerate elementary particles along a straight path. Circular accelerators, such as the Tevatron, the LEP, and the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), use circular paths. Circular geometry has significant advantages at energies up to and including tens of GeV: With a circular design, particles can be effectively accelerated over longer distances. Also, only a fraction of the particles brought onto a collision course actually collide. In a linear accelerator, the remaining particles are lost; in a ring accelerator, they keep circulating and are available for future collisions. The disadvantage of circular accelerators is that charged particles moving along bent paths will necessarily emit electromagnetic radiation known as synchrotron radiation. Energy loss through synchrotron radiation is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the mass of the particles in question. That is why it makes sense to build circular accelerators for heavy particles—hadron colliders such as the LHC for protons or, alternatively, for lead nuclei. An electron–positron collider of the same size would never be able to achieve the same collision energies. In fact, energies at the LEP, which used to occupy the tunnel now given over to the LHC, were limited to 209 GeV by energy loss via synchrotron radiation.
Even though the nominal collision energy at the LHC will be higher than the ILC collision energy (14,000 GeV for the LHC[4] vs. ~500 GeV for the ILC), measurements could be made more accurately at the ILC. Collisions between electrons and positrons are much simpler to analyze than collisions in which the energy is distributed among the constituent quarks, antiquarks and gluons of baryonic particles. As such, one of the roles of the ILC would be making precision measurements of the properties of particles discovered at the LHC.
ILC physics and detectors
It is widely expected that effects of physics beyond that described in the current Standard Model will be detected by experiments at the proposed ILC.[5] In addition, particles and interactions described by the Standard Model are expected to be discovered and measured. At the ILC physicists hope to be able to:
- Measure the mass, spin, and interaction strengths of the Higgs boson
- If existing, measure the number, size, and shape of any TeV-scale extra dimensions
- Investigate the lightest supersymmetric particles, possible candidates for dark matter
To achieve these goals, new generation particle detectors are necessary.
Merging of regional proposals into a worldwide project
In August 2004, the International Technology Recommendation Panel (ITRP) recommended[6] a superconducting radio frequency technology for the accelerator. After this decision the three existing linear collider projects – the Next Linear Collider (NLC), the Global Linear Collider (GLC) and Teraelectronvolt Energy Superconducting Linear Accelerator (TESLA) – joined their efforts into one single project (the ILC). Physicists are now working on the detailed design of the accelerator. Steps ahead include obtaining funding for the accelerator, and choosing a site. In August 2007, the Reference Design Report for the ILC was released.[7]
In March 2005, the International Committee for Future Accelerators (ICFA) announced the appointment of Prof. Barry Barish as the Director of the Global Design Effort. Barry Barish was director of the LIGO Laboratory at Caltech from 1997 to 2005.
Design
The electron source for the ILC will use 2-nanosecond laser light pulses to eject electrons from a photocathode, a technique allowing for up to 80% of the electrons to be polarized; the electrons then will be accelerated to 5 GeV in a 370-meter linac stage. Synchrotron radiation from high energy electrons will produce electron-positron pairs on a titanium-alloy target, with as much as 60% polarization; the positrons from these collisions will be collected and accelerated to 5 GeV in a separate linac.
To compact the 5 GeV electron and positron bunches to a sufficiently small size to be usefully collided, they will circulate for 0.1–0.2 seconds in a pair of damping rings, 3.24 km in circumference, in which they will be reduced in size to 6 mm in length and a vertical and horizontal emittance of 2 pm and 0.6 nm, respectively.
From the damping rings the particle bunches will be sent to the superconducting radio frequency main linacs, each 11 km long, where they will be accelerated to 250 GeV. At this energy each beam will have an average power of about 5.3 megawatts. Five bunch trains will be produced and accelerated per second.
To maintain a sufficient luminosity to produce results in a reasonable time frame after acceleration the bunches will be focused to a few nanometers in height and a few hundred nanometers in width. The focused bunches then will be collided inside one of two large particle detectors.
-
An interior view of the niobium superconducting radio frequency cavity
-

A cryomodule being tested at Fermilab
-

Cross section of the cryomodule. A large tube at the center is Helium gas return pipe. The closed tube below it is the beam axis.
-

A flange of the cryomodule is used to connect instrumentation wires and cables.
- ^ The International Linear Collider Technical Design Report 2013. International Linear Collider. 2013. Retrieved 14 August 2015.
Proposed sites
Presently three sites for the International Linear Collider are leading contenders at established High Energy Physics center in Europe.[8] At CERN in Geneva the tunnel is located deep underground in non-permeable bedrock. This site is considered favorable for a number of practical reasons but due to the LHC the site is disfavored. At DESY in Hamburg the tunnel is close to the surface in water saturated soil. Germany leads Europe for scientific funding and is therefore considered reliable in terms of funding. At JINR in Dubna the tunnel is close to the surface in non-permeable soil. Dubna has a pre-accelerator complex which could be easily adapted for the needs for the ILC. But all three are more or less well suited for housing a Linear Collider and one has ample choice for a site selection process in Europe.
Outside Europe a number of countries have expressed interest. Japan presently receives a large amount of funding for the neutrino activities, such as the T2K experiment, so it is disfavored although 20 huge caverns with access tunnels have already been constructed in Japan for hydroelectric power plants (e.g. the Kannagawa Hydropower Plant). With the impending closure of the Tevatron some groups within the USA have expressed interest, with Fermilab being a favored site because of the facilities and manpower already present. Much of the speculated interest from other countries is hearsay from within the scientific community and very few facts have been published officially. The information presented above is a summary of that contained in the International Workshop on Linear Colliders 2010 (ECFA-CLIC-ILC Joint Meeting) at CERN.[9]
The 2008 economic crisis led the United States and United Kingdom to cut funds to the collider project,[10] leading to speculation that Japan may be the most likely host for the International Linear Collider.[11] On August 23, 2013, the Japanese high-energy physics community's site evaluation committee proposed it should be located in the Kitakami Mountains of the Iwate and Miyagi Prefectures.[12]
Cost and time estimates
The Reference Design Report estimates the cost of building the ILC, excluding R&D, prototyping, land acquisition, underground easement costs, detectors, contingencies, and inflation, at US$6.75 billion [13] (in 2007 prices). From formal project approval, completion of the accelerator complex and detectors is expected to require seven years. The host country would be required to pay $1.8 billion for site-specific costs like digging tunnels and shafts and supplying water and electricity.
Former U.S. Secretary of Energy Steven Chu estimates the total cost to be US$25 billion. ILC Director Barish says this is likely to be an overestimate. Other Department of Energy officials have estimated a $20 billion total.[14]
Notes
- ↑ "The International Linear Collider – Gateway to the Quantum Universe" (PDF). ILC Community. 2007-10-18. Retrieved 2009-05-21.
- ↑ Hamish Johnston. "Where should the International Linear Collider be built?". physicsworld.com. Retrieved 2012-08-02.
- ↑ "The new particle accelerator ILC will not be completed before 2026, says François Richard (spanish)". 2012-06-11. Retrieved 2012-08-02.
- ↑ Since the actual collisions happen between the constituent of protons—quarks, antiquarks and gluons—the effective energy for collisions will be lower than 14,000 GeV but still higher than 500 GeV), a typical collision at the LHC will be of higher energy than a typical ILC collision.
- ↑ G. Aarons; et al. (2007), International Linear Collider Reference Design Report Volume 2: Physics at the ILC (PDF), arXiv:0709.1893
 , Bibcode:2007arXiv0709.1893D
, Bibcode:2007arXiv0709.1893D - ↑ "Final International Technology Recommendation Panel report" (PDF). ICFA (International Committee for Future Accelerators). 2004. Retrieved 2012-11-19.
- ↑ "ILC Reference Design Report" (PDF). ILC Global Design Effort and World Wide Study. August 2007. Retrieved 2009-05-21.
- ↑ Wilhelm Bialowons, John Andrew Osborne and Grigori Shirkov (March 31, 2010). "Siting Study for European ILC Sites" (PDF). ILC-HiGrade-Report-2010-004-1.
- ↑ "International Workshop on Linear Colliders 2010". 22 October 2010.
- ↑ "Accelerator plans stalled after US and UK cuts". Nature. 9 January 2008.
- ↑ "Japan in pole position to host particle smasher". Nature. 14 December 2012.
- ↑ Kelen Tuttle and Kathryn Jepsen (August 23, 2013). "Japan selects candidate site for linear collider". Symmetry Magazine. Fermilab. Retrieved 2013-08-23.
- ↑ Overbye, Dennis (2007-02-08). "Price of Next Big Thing in Physics: $6.7 Billion". NYTimes. Retrieved 2010-05-05.
- ↑ "Chu Pegs ILC Cost at $25 Billion". ScienceInsider. 2009. Archived from the original on January 5, 2010.
External links
- International Linear Collider Website
- ILC NewsLine
- Karl Van Bibber about the NLC
- In symmetry magazine:
- Special issue, August 2005
- "out of the box: designing the ILC", March 2006
- New York Times article
- Science Magazine article
- Scientific American article preview
- 1600 International Linear Collider Article
- arXiv:
- The International Linear Collider Technical Design Report - Volume 1: Executive Summary
- The International Linear Collider Technical Design Report - Volume 2: Physics
- The International Linear Collider Technical Design Report - Volume 3.I: Accelerator R&D in the Technical Design Phase
- The International Linear Collider Technical Design Report - Volume 3.II: Accelerator Baseline Design
- The International Linear Collider Technical Design Report - Volume 4: Detectors