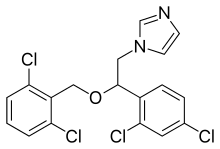
Isoconazole
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | D01AC05 (WHO) G01AF07 (WHO) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 27523-40-6 |
| PubChem (CID) | 3760 |
| DrugBank |
DB08943 |
| ChemSpider | 3629 |
| UNII |
GRI7WFR424 |
| KEGG | D04624 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:82865 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1571863 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.044.084 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H14Cl4N2O |
| Molar mass | 416.127 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
Isoconazole is an azole antifungal drug and could inhibit gram positive bacteria.[1][2] Nigerian and British medical researchers found that for foot and vaginal infections, isoconazole has a similar effectiveness to clotrimazole.[3][4] Isoconazole nitrate may be used in combination with corticosteroid diflucortolone to increase its bioavailability.[1]
References
- 1 2 Veraldi, Stefano (May 2013). "Isoconazole nitrate: a unique broad-spectrum antimicrobial azole effective in the treatment of dermatomycoses, both as monotherapy and in combination with corticosteroids". Mycoses. 56 Suppl 1: 3–15. doi:10.1111/myc.12054. ISSN 1439-0507. PMID 23574019.
- ↑ The Merck Index, 12th Edition, 5176
- ↑ Oyeka, C.A.; Gugnani H.C. (1992). "Isoconazole nitrate versus clotrimazole in foot and nail infections due to Hendersonula toruloidea, Scytalidium hyalinum and dermatophytes.". Mycoses. 35 (11-12): 357–61. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0507.1992.tb00894.x. PMID 1302811.
- ↑ Cohen, L. (1984). "Single dose treatment of vaginal candidosis: comparison of clotrimazole and isoconazole.". Retrieved 2008-05-23.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/8/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.