Isoliquiritigenin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
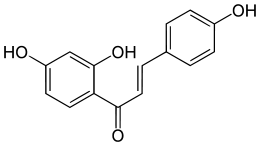
| IUPAC name
(E)-1-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one | |
| Other names
6'-deoxychalcone 2',4,4'-Trihydroxychalcone 4,2',4'-Trihydroxychalcone 4'2'4'-trihydroxychalcone 2',4',4-Trihydroxychalcone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 961-29-5 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:310312 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL129795 |
| ChemSpider | 553829 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.202.617 |
| EC Number | 237-316-5 |
| KEGG | C08650 |
| PubChem | 638278 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H12O4 | |
| Molar mass | 256.25 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Isoliquiritigenin is a phenolic chemical compound found in licorice. It is under experimentation phase testing for use as a cancer treatment and as an aide for cocaine addiction. It is a sirtuin-activating compound.
Metabolism
The enzyme 6'-deoxychalcone synthase uses malonyl-CoA, 4-coumaroyl-CoA, NADPH, and H+ to produce CoA, isoliquiritigenin, CO2, NADP+, and H2O.
The enzyme isoliquiritigenin 2'-O-methyltransferase further transforms isoliquiritigenin into 2'-O-methylisoliquiritigenin.
Mechanism of action
Isoliquiritigenin has been found to potent (65 times higher affinity than diazepine) GABA-A benzodiapine receptor positive allosteric modulator.[1]
References
- ↑ Cho, S; Kim, S; Jin, Z; Yang, H; Han, D; Baek, N. I.; Jo, J; Cho, C. W.; Park, J. H.; Shimizu, M; Jin, Y. H. (2011). "Isoliquiritigenin, a chalcone compound, is a positive allosteric modulator of GABAA receptors and shows hypnotic effects". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 413 (4): 637–42. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.09.026. PMID 21945440.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/10/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.