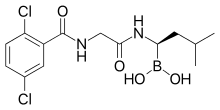
Ixazomib
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ninlaro |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | ninlaro |
| Routes of administration | Oral (capsules) |
| ATC code | L01XX50 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 58%[1] |
| Protein binding | 99% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP: 3A4 (42%), 1A2 (26%), 2B6 (16%) and others) |
| Biological half-life | 9.5 days |
| Excretion | Urine (62%), feces (22%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | MLN2238 |
| CAS Number | 1072833-77-2 |
| PubChem (CID) | 25183872 |
| ChemSpider | 25027391 |
| UNII | 71050168A2 |
| KEGG | D10130 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:90942 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H19BCl2N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 361.03 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Ixazomib (trade name Ninlaro) is a drug for the treatment of multiple myeloma, developed by Takeda. It acts as a proteasome inhibitor and has orphan drug status in the US.
On November 20, 2015, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved ixazomib for use in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone for the treatment of multiple myeloma after at least one prior therapy.[2]
Mechanism
Ixazomib is a peptide analogue that reversibly inhibits the protein proteasome subunit beta type-5 (PSMB5), which is part of the 20S proteasome complex.[3]
Chemistry
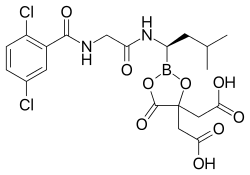
Ixazomib citrate—a prodrug for ixazomib
Ixazomib citrate is a prodrug which rapidly hydrolyzes under physiological conditions to its biologically active form, ixazomib.[1]
References
- 1 2 "Ninlaro (ixazomib) Capsules, for Oral Use. Full Prescribing Information" (PDF). NINLARO (ixazomib) For Healthcare Professionals. Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited. Retrieved 21 November 2015.
- ↑ "Press Announcements — FDA approves Ninlaro, new oral medication to treat multiple myeloma". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 24 April 2016.
- ↑ KEGG: Ixazomib
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/17/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.