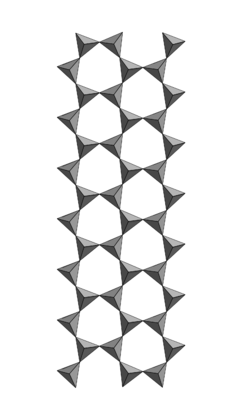
Jimthompsonite
| Jimthompsonite | |
|---|---|
|
Jimthompsonite structure | |
| General | |
| Category | Inosilicates |
| Formula (repeating unit) | (Mg,Fe2+)5Si6O16(OH)2 |
| Strunz classification | 9.DF.05 |
| Crystal system | Orthorhombic |
| Crystal class |
Dipyramidal (mmm) H-M symbol: (2/m 2/m 2/m) |
| Space group | Pbca |
| Unit cell |
a = 18.626, b = 27.23 c = 5.297 [Å]; Z = 8 |
| Identification | |
| Color | Colorless to very light pinkish brown |
| Crystal habit | Radiating sprays and fibrous intergrowths |
| Cleavage | Perfect on {210} with 38° and 142° intersecting angle |
| Mohs scale hardness | 2-2.5 |
| Specific gravity | 3.02 (calculated) |
| Optical properties | Biaxial (-) |
| Refractive index | nα = 1.605 nβ = 1.626 nγ = 1.633 |
| Birefringence | δ = 0.028 |
| 2V angle | 62° measured |
| References | [1][2][3] |
Jimthompsonite is a magnesium iron silicate mineral with formula: (Mg,Fe2+)5Si6O16(OH)2. It is a triple chain silicate (or inosilicate) along with clinojimthompsonite and chesterite. They were described in 1977 by Burham and Veblen. They attracted great mineralogical attention because they were the first examples of new chain silicate structures among a large group known as biopyriboles whose name is derived from the words biotite, pyroxene, and amphiboles.
James B. Thompson, Jr. postulated the existence of the new biopyroles in 1970. The theory proved correct when jimthompsonite, clinojimthompsonite and chesterite were discovered in the Carlton Quarry in Windsor County, Vermont in 1977.[2]
The new minerals are found intergrown with the amphiboles anthophyllite and cummingtonite in sprays up to 5 cm long. They are all colorless to pale pinkish-brown and transparent. As for pyroxene and amphiboles, the type of chain structure dictates the angle between the two distinctive cleavages.
The cleavages of jimthompsonite are at 142 degrees and 38 degrees, and 135 degrees and 45 for chesterite; compared to the cleavage angles of pyroxene at about 94 degrees and 86 degrees and amphibole about 124 and 56 degrees.
Composition
The chemical formula of jimthompsonite is (Mg,Fe++)5Si6O16(OH)2. Veblen and Durham determined the percentages of jimthompsonite as follows:[3]
- Magnesium 14.71% Mg 24.40% MgO
- Iron 11.27% Fe 14.50% FeO
- Silicon 27.20% Si 58.20% SiO2
- Hydrogen 0.33% H 2.91% H2O
- Oxygen 46.49% O
Some of the other characteristics of jimthompsonite are that it has an orthorhombic crystal system dipyramidal with H-M symbol (2/m 2/m 2/m) and space group: Pbca. It has a perfect cleavage, its colorless to pink brown with a density of 3.03 g/cm3 and hardness of 2-2.5 gypsum. It has a white streak and silky-pearly luster.
Origin
It is found in the Carleton talc quarry, near Chester, Windsor County, Vermont, US. The name triple chain silicate comes from a wide complex chain structure as silicon being the most dominant element in its composition. It was named for James Burleigh Thompson, Jr. (born 1921), petrologist of Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts, US.
References
Further reading
- Clements, R.; Robinson D. (1996). "The Carlton quarry, Chester, Windsor, County, Vermont". Rocks & Minerals 71:231-35.
- Hiromi Konishi; Huifang Xu; Dymek, R. F. (2010). "High Resolution Tem study of Jimthompsinite and Chesterite and chain-width disorder in Archean ultramafic rocks from Isua, West Greenland". American Mineralogist; 95:73–80.
- Thompson, J. B., Jr (1970). "Geometrical possibilities for amphibole structures: model Biopyriboles". American Mineralogist 55:292-93
- Thompson, J. B., Jr. (1978). "Biopyriboles and polysomatic series". American Mineralogist 63:239-49.
- Veblen, D. R.; Buseck, P. R. (1980). "Microstructures and reaction mechanisms in biopyriboles". American Mineralogist 65:599-623.
- Veblen, D. R.; Buseck, P. R.; Burnham, C. W. (1977). "Asbestiform Chain Silicates: New Minerals and Structural Groups". Science. 198 (4315): 359–365. doi:10.1126/science.198.4315.359. PMID 17809428.
External links
- J is for Jimthompsonite in Geology Word of the Week