Kadsura japonica
| Kadsura japonica | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| Order: | Austrobaileyales |
| Family: | Schisandraceae |
| Genus: | Kadsura |
| Species: | K. japonica |
| Binomial name | |
| Kadsura japonica (L.) Dunal. | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Kadsura japonica, commonly known as the Kadsura vine or simply Kadsura, is a plant species native to Japan (Honshū, Kyūshū and the Ryukyu Islands) in woodlands.. The larvae of the moth Caloptilia kadsurae feed on K. japonica in the main Japanese islands and Ryukyu Islands.
Description
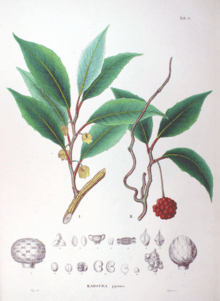
Kadsura japonica is cultivated as an ornamental plant in gardens, and also has edible fruits that can be eaten raw or cooked.[1] They grow from 8 feet (2.4 m) to 15 feet (4.6 m). It is a evergreen with deep green, glossy leaves that turn slightly red in autumn. Its fruits are very bright scarlet[2] and it has white dioecious flowers.[3][4] This plant contains 1-3 seeds. Apex is acuminate to acuminate. Leaves are variegated, shiny green and irregularly edged in white. Flowers are cup shaped and have red berries in spring. Petioles are 0.6- 2.3 cm long. 5-8 secondary veins on each midvein in the leaves. This plants can be both monoecious and dioecious.[5][6]
Taxonomy
There are 22 species of this genus Kadsura. Kadsura japonica is an ornamental cultivated species. Kadsura is one of the only two genera of the family Schisandraceae. Cultivars include fukerin, piper, variegata.[7]
Distribution and habitat
It is found in the tropical and subtropical habitats and can be grown as an indoor plant. This plant is found in Japan, southern China, southern Korea and eastern Asia. It can be in habitats such as woodland garden, found in both the sun and shade. It grows in a moderate and fertile soil. It needs a neutral or acidic soil, that is adaptable and well-drained. This plant mostly doesn’t need a bright sunlight. In autumn, the shoot of the plant becomes very long and forms layers. It is a climber on woodland trees. It is found at an elevation of 500-2000m in some province of China, Fujian and Taiwan.[8]
Uses
It is used for medical purposes, that can be beneficial for fighting against kidney diseases. The other use for this plant is fighting against cough, asthma and other respiratory ailments. Fruit from this plant can be used for edible purposes, either eaten raw or cooked. Extract from the plant is used for paper manufacturing. Material extracted from this plant is used for hair dressing. Extract from this plant is also used for traditional Japanese washi paper making.[9]
References
- ↑ Pink, A. (2004). Gardening for the Million. Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation.
- ↑ "Illiciales". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 9 February 2014.
- ↑ "Kadsura japonica". NC State University. Retrieved 9 February 2014.
- ↑ pfaf.org: Kadsura matsudai (Kadsura japonica)
- ↑ "Kadsura japonica". Useful Tropical Plants. Useful Tropical Plants Database. August 16, 2016. Retrieved October 15, 2016.
- ↑ "Kadsura japonica 'Variegata'". Plant lust. Plant lust. Retrieved October 15, 2016.
- ↑ "Illiciales". Encyclopӕdia Britannica. Encyclopӕdia Britannica, Inc. June 30, 2008. Retrieved October 15, 2016.
- ↑ "Kadsura japonica". Useful Tropical Plants. Useful Tropical Plants Database. August 16, 2016. Retrieved October 15, 2016.
- ↑ "Kadsura japonica". Useful Tropical Plants. Useful Tropical Plants Database. August 16, 2016. Retrieved October 15, 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kadsura japonica. |