Kempen, Germany
| Kempen | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Old School Street | ||
| ||
 Kempen | ||
Location of Kempen within Viersen district 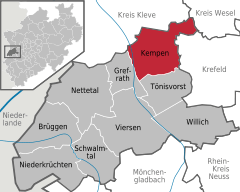
 | ||
| Coordinates: 51°21′57″N 6°25′10″E / 51.36583°N 6.41944°ECoordinates: 51°21′57″N 6°25′10″E / 51.36583°N 6.41944°E | ||
| Country | Germany | |
| State | North Rhine-Westphalia | |
| Admin. region | Düsseldorf | |
| District | Viersen | |
| Government | ||
| • Mayor | Volker Rübo (CDU) | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 68.79 km2 (26.56 sq mi) | |
| Population (2015-12-31)[1] | ||
| • Total | 34,837 | |
| • Density | 510/km2 (1,300/sq mi) | |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) | |
| Postal codes | 47906 | |
| Dialling codes | 0 21 52 | |
| Vehicle registration | VIE | |
| Website | www.kempen.de | |
Kempen (Limburgish: Kempe) is a town in the district of Viersen, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is situated approximately 30 km northwest of Düsseldorf, and 20 km east of Venlo.
Notable persons
Kempen is the birthplace of Thomas à Kempis.
Thomas was born in either 1379 or 1380 in Kempen. His birthplace was on the Kirchplatz (church square) about where the house "St. Marien 11" stands today. Thomas was the second son of the craftsman Johann Hemerken and his wife Gertrud Kuyt, who was most probably a teacher.
In Kempen, Thomas visited the Latin School until the age of 12. Afterwards, he left Kempen in order to visit the town school in Deventer, which had a very good reputation and was most likely therefore known on the Lower Rhine. The school served as a preparatory institution for university study and taught mainly grammar, logic, ethics and philosophy.
In 1836, the Thomas Society was founded in Kempen in order to foster the memory of the greatest son of the city. In the twentieth century, there have been two other foundations: in 1979, the married couple Heinrich and Christine Kiefer founded the Thomas Foundation and in 1987, the Provost’s parish, the town of Kempen and the Thomas Society jointly founded the Thomas Archive, which can be found in the Cultural Forum of the Franciscan Monastery.
- John Brugman (?–1473), Franciscan friar and preacher in Flanders
- Wilhelm Hünermann (1900–1975), German priest and writer
- Isabel Varell (born 1961), German actress and singer
- Bernhard van Treeck (born 1964), German psychiatrist and author
- Tobias Koch (born 1968), German pianist
History
- 1186 First mention in official documentation of Kempen as a place - the sovereign until 1794 is the Archbishop (electoral prince) of Cologne
- around 1290 Kempen is rebuilt as a fortified town
- 03.11.1294 First confirmation of Kempen as a town in official documentation
- 15th century town blooms economically and culturally (population of approx. 4,200)
- 1542/43 Kempen is the centre of the Reformation for the Lower Rhine
- 1579 The plague costs the town almost half of its inhabitants
- 1642 Kempen is conquered and destroyed by the allied French, Hessian and Weimar troops during the "Hessen War" (Thirty Years' War)
- 1794-1814 Kempen is under French rule. In the Département de la Roer established in 1797, Kempen becomes a canton seat in 1798 and a French town in 1801.
- 1815 After the Congress of Vienna, Kempen becomes Prussian and is the county seat
- 1929 Due to local reforms, Kempen becomes the administrative seat of the county of Kempen-Krefeld
- starting from 1966 Restoration of the old town
- 1970 Communal restructuring: The communities of Hüls, St. Hubert, Tönisberg and Schmalbroich join Kempen along with the localities of St. Peter and Unterweiden to form a single town
- 1975 In further local reforms, Hüls is assigned to the city of Krefeld. The county of Viersen is formed and Kempen becomes part of "Kreis Viersen"
- 1984 The county seat is transferred from Kempen to Viersen.
- 1987 A cultural forum is opened in the Franciscan monastery after comprehensive restoration and renovation work.
- 03.11.1994 700-year jubilee of the confirmation of Kempen as a town
Twin towns
- Wambrechies, France, since 1972
- Orsay, France, since 1973
- East Cambridgeshire, England, since 1978
- Werdau, Germany, since 1990
Gallery
-
Kempen, view in a street
-
Kempen, church
-
Kempen, towngate: das Kuhtor
-
Kempen, Lutheran church (Thomas Church)
-
.jpg)
Kempen, Hessenmühle
-

Kempen, Burg
References
- ↑ "Amtliche Bevölkerungszahlen". Landesbetrieb Information und Technik NRW (in German). 18 July 2016.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Wood, James, ed. (1907). "article name needed". The Nuttall Encyclopædia. London and New York: Frederick Warne.
