Kepler-452
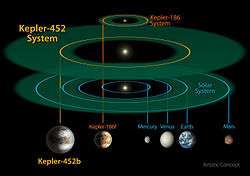 Artist's impression of the Kepler-452 and Kepler-186 systems compared to the inner Solar System, with their respective habitable zones shown. | |
| Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Evolutionary stage | Main sequence |
| Spectral type | G2V |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
| Constellation | Cygnus |
| Right ascension | 19h 44m 0.9s[1] |
| Declination | +44° 16′ 39.2″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 13.426[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Distance | 1400 ly (430 pc) |
| Details | |
| Mass | 1.037+0.054 −0.047 M☉ |
| Radius | 1.11+0.15 −0.09 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1.2 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.32 ± 0.09 cgs |
| Temperature | 5757 ± 85 K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | 0.21 ± 0.09 dex |
| Age | 6 ± 2 Gyr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| Exoplanet Archive | 452-b data |
Kepler-452 is a G-type main-sequence star located about 1400 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Cygnus.[3] It has a similar temperature to that of the Sun, but it is 20 percent brighter, 3.7 percent more massive and is 11 percent larger.[4][5] It is approximately six billion years old, 1.5 billion years older than the Sun and also has a much higher metallicity.[6] Thus, Kepler-452 can be considered a solar twin, however its age pushes it more back towards the "solar analog" criteria.[lower-alpha 1]
Nomenclature and history

Prior to Kepler observation, Kepler-452 had the 2MASS catalogue number 2MASS 19440088+4416392. In the Kepler Input Catalog it has the designation of KIC 8311864, and when it was found to have a transiting planet candidate it was given the Kepler object of interest number of KOI-7016.
Planetary candidates were detected around the star by NASA's Kepler Mission, a mission tasked with discovering planets in transit around their stars. The transit method that Kepler uses involves detecting dips in brightness in stars. These dips in brightness can be interpreted as planets whose orbits pass in front of their stars from the perspective of Earth, although other phenomenon can also be responsible which is why the term planetary candidate is used.[9]
Following the acceptance of the discovery paper, the Kepler team provided an additional moniker for the system of "Kepler-452".[10] The discoverers referred to the star as Kepler-452, which is the normal procedure for naming the exoplanets discovered by the spacecraft.[6] Hence, this is the name used by the public to refer to the star and its planet.
Candidate planets that are associated with stars studied by the Kepler Mission are assigned the designations ".01" etc. after the star's name, in the order of discovery.[2] If planet candidates are detected simultaneously, then the ordering follows the order of orbital periods from shortest to longest.[2] Following these rules, there was only one candidate planet detected, with an orbital period of 384.843 days. The name Kepler-452 derives directly from the fact that the star is the catalogued 452nd star discovered by Kepler to have confirmed planets.
The designation b, derives from the order of discovery. The designation of b is given to the first planet orbiting a given star, followed by the other lowercase letters of the alphabet.[11] In the case of Kepler-452, there was only one planet, so only the letter b is used.
Stellar characteristics
Kepler-452 is a G-type star that is approximately 104% the mass of and 111% the radius of the Sun. It has a temperature of 5757 K and is roughly 6 billion years old. In comparison, the Sun is about 4.6 billion years old[12] and has a temperature of 5778 K.[13]
The star is metal-rich, with a metallicity ([Fe/H]) of about 0.21, or about 162% of the amount of iron and other heavier metals found in the Sun.[6] The star's luminosity is somewhat normal for a star like Kepler-452, with a luminosity of around 120% of that of the solar luminosity.
The star's apparent magnitude, or how bright it appears from Earth's perspective, is 13.426. Therefore, it is too dim to be seen with the naked eye.
Planetary system
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (days) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | 5 ± 2[14] M⊕ | 1.046+0.019 −0.015 |
384.843+0.007 −0.012 |
— | 89.806+0.134 −0.049° |
1.5+0.32 −0.22 R⊕ |
The star hosts one confirmed exoplanet, Kepler-452b, discovered in July 2015 by the Kepler spacecraft. This planet is mostly known for its characteristics similar to Earth, most notably its size, orbit and stellar flux. It is the first potentially rocky super-Earth[15] planet discovered orbiting within the habitable zone of a star very similar to the Sun.[4] It may even have a surface temperature similar to that of Earth (the planet has a equilibrium temperature of ~265 K (−8 °C; 17 °F), and Earth's equilibrium temperature is only 10 K cooler than this). However its star is 6 billion years old (roughly 1.5 billion years older than the Sun). Due to this, Kepler-452b is receiving roughly 10% more stellar radiation than the Earth does today. If Kepler-452b is a rocky planet, it may be subject to a runaway greenhouse effect. However, because of its mass (estimated to be about 5 M⊕), it may be able to prevent succumbing to the runaway greenhouse for a limited amount of time (at most about 500 million years). Nevertheless, the planet is one of the most Earth-like planets discovered so far by the Kepler team.
Sun comparison
This chart compares the Sun to Kepler-452.
| Identifier | J2000 Coordinates | Distance (ly) |
Stellar Class |
Temperature (K) |
Metallicity (dex) |
Age (Gyr) |
Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right ascension | Declination | |||||||
| Sun | — | — | 0.00 | G2V | 5,778 | +0.00 | 4.6 | [8] |
| Kepler-452 [16] | 19h 44m 00.89s | +44° 16′ 39.2″ | 1,400 | G2V | 5,757 | +0.21 | 6.0 | [17] |
Footnotes
- ↑ An exact solar twin would be a G2V star with a 5778 K temperature, be 4.6 billion years old, with the correct metallicity and a 0.1% solar luminosity variation.[7][8]
References
- 1 2 3 "NASA Exoplanet Archive – Confirmed Planet Overview – Kepler-452b". NASA Exoplanet Archive. 2015. Retrieved 23 July 2015.
- 1 2 3 "Kepler Input Catalog search result". Space Telescope Science Institute. Retrieved 25 July 2015.
- ↑ Witze, Alexandra (23 July 2015). "NASA spies Earth-sized exoplanet orbiting Sun-like star". Nature. Retrieved 23 July 2015.
- 1 2 Chou, Felicia; Johnson, Michelle (23 July 2015). "NASA's Kepler Mission Discovers Bigger, Older Cousin to Earth" (Press release). NASA. Retrieved 23 July 2015.
- ↑ Rincon, Paul (23 July 2015). "'Earth 2.0' found in Nasa Kepler telescope haul". BBC. Retrieved 23 July 2015.
- 1 2 3 Jenkins, Jon M.; Twicken, Joseph D.; Batalha, Natalie M.; Caldwell, Douglas A.; Cochran, William D.; Endl, Michael et al. (2015). "Discovery and validation of Kepler-452b: A 1.6 R⨁ super Earth exoplanet in the habitable zone of a G2 star". The Astronomical Journal. Institute of Physics. 105 (2). arXiv:1507.06723
 . Bibcode:2015AJ....150...56J. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/150/2/56.
. Bibcode:2015AJ....150...56J. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/150/2/56. - ↑ "Solar Variability and Terrestrial Climate - NASA Science". Retrieved 8 January 2013.
- 1 2 Williams, David R. (2004). "Sun Fact Sheet". NASA. Retrieved 23 June 2009.
- ↑ Morton, Timothy; Johnson, John (23 August 2011). "On the Low False Positive Probabilities of Kepler Planet Candidates". The Astrophysical Journal. 738 (2): 170. arXiv:1101.5630
 . Bibcode:2011ApJ...738..170M. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/738/2/170. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
. Bibcode:2011ApJ...738..170M. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/738/2/170. Retrieved 2 March 2014. - ↑ NASA (27 January 2014). "Kepler – Discoveries – Summary Table". NASA. Retrieved 1 March 2014.
- ↑ Hessman, Frederic V.; Dhillon, Vikram S.; Winget, Donald E.; Schreiber, Matthias R.; Horne, Keith; Marsh, Thomas R.; Guenther, Eike W.; Schwope, Axel D.; Heber, Ulrich (2010). "On the naming convention used for multiple star systems and extrasolar planets". arXiv:1012.0707
 [astro-ph.SR].
[astro-ph.SR]. - ↑ Williams, Matt (9 May 2016). "Life Cycle of the Sun". Universe Today. Retrieved 17 August 2016.
- ↑ Cain, Fraser (23 December 2015). "What Color is the Sun?". Universe Today. Retrieved 17 August 2016.
- ↑ "NASA's Kepler Mission Discovers Bigger, Older Cousin to Earth". National Aeronautics and Space Administration. 23 July 2015. Retrieved 10 June 2016.
- ↑ "The Habitable Exoplanets Catalog – Planetary Habitability Laboratory @ UPR Arecibo". upr.edu.
- ↑ Kepler-452 at SIMBAD - Ids - Bibliography - Image.
- ↑ "Planet Kepler-452 b (sic)". Retrieved 6 July 2016.