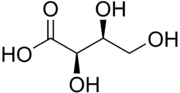
Threonic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2R,3S)-2,3,4-Trihydroxybutanoic acid | |
| Other names
Threonate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3909-12-4 (D/L) 20246-26-8 (D) 7306-96-9 (L) | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| PubChem | 5460407 |
| UNII | NTD0MI8XRT (D/L) 75B0PMW2JF (L) |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H8O5 | |
| Molar mass | 136.10 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Threonic acid is a sugar acid derived from threose. The L-isomer is a metabolite of ascorbic acid (vitamin C).[1] One study suggested that because L-threonate inhibits DKK1 expression in vitro, it may have potential in treatment of androgenic alopecia.[2]
References
- ↑ S Englard and S Seifter (1986). "The Biochemical Functions of Ascorbic Acid". Annual Review of Nutrition. 6: 365–406. doi:10.1146/annurev.nu.06.070186.002053. PMID 3015170.
- ↑ Kwack, M. H.; Ahn, J. S.; Kim, M. K.; Kim, J. C.; Sung, Y. K. (2010). "Preventable effect of L-threonate, an ascorbate metabolite, on androgen-driven balding via repression of dihydrotestosteroneinduced dickkopf-1 expression in human hair dermal papilla cells". BMB Reports. 43 (10): 688–692. doi:10.5483/BMBRep.2010.43.10.688. PMID 21034532.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/21/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.